Week 7 [Mar 4]
- The Project List Page will be up this week.
If your photo or your UI mock-up does not appear in the page, you have not followed our instructions correctly. 'Close enough' is sometimes not 'good enough'. Please rectify before v1.1 deadline. In particular,
-
Please follow our guidelines for your photo. If not, the photo will not serve its intended purpose (i.e., for others to identify you).
-
Please limit the
Ui.pngto one screenshot only, so that your UI mockup takes roughly the same amount of space as other teams' in the Teams Page. -
Peer Evaluation Round 1 will open on TEAMMATES. If you do not submit feedback responses, you will forfeit participation marks that you earned based on feedback ratings received from others.
-
An anonymous survey to submit feedback about the teaching team will open on LumiNUS. Please take a few minutes to give feedback to your tutors.
v1.1 milestone deadline is coming up soon: Refer to v1.1 instructions carefully and try to follow as closely as you can. However, there is no lower bar on the code changes you need to do. Even a tiny change is acceptable. Use that flexibility to control your workload.
[W7.1] Association Classes
Can explain the meaning of association classes
An association class represents additional information about an association. It is a normal class but plays a special role from a design point of view.
A Man class and a Woman class is linked with a ‘married to’ association and there is a need to store the date of marriage. However, that data is related to the association rather than specifically owned by either the Man object or the Woman object. In such situations, an additional association class can be introduced, e.g. a Marriage class, to store such information.
Implementing association classes
There is no special way to implement an association class. It can be implemented as a normal class that has variables to represent the endpoint of the association it represents.
In the code below, the Transaction class is an association class that represent a transaction between a Person who is the seller and another Person who is the buyer.
class Transaction{
//all fields are compulsory
Person seller;
Person buyer;
Date date;
String receiptNumber;
Transaction (Person seller, Person buyer, Date date, String receiptNumber){
//set fields
}
}
Which one of these is the suitable as an Association Class?
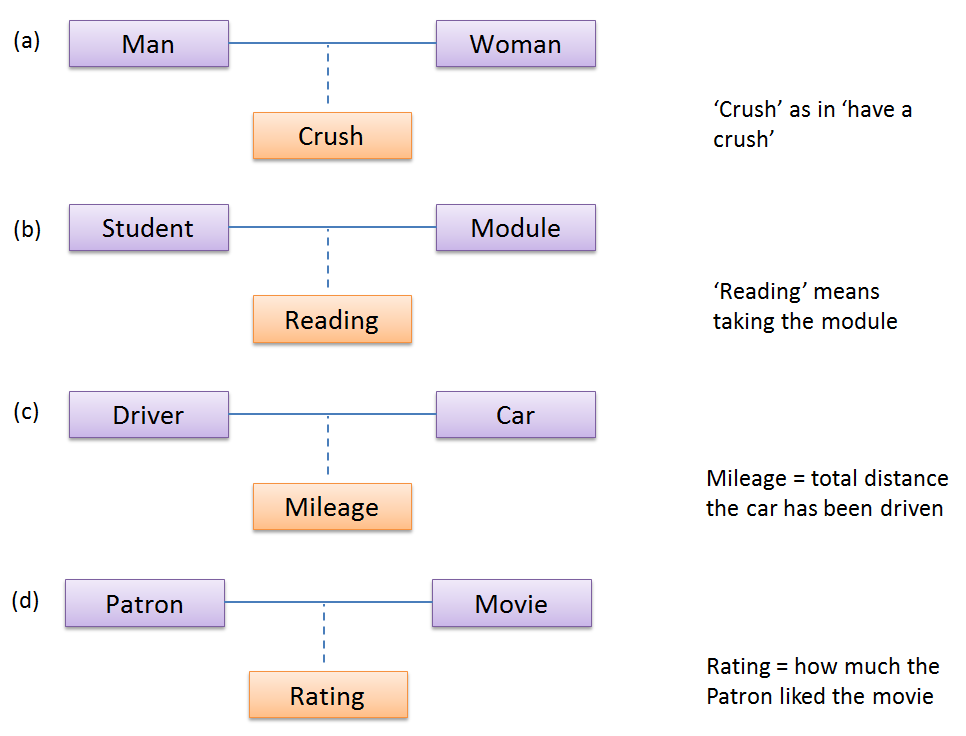
- a
- b
- c
- d
(a)(b)(c)(d)
Explanation: Mileage is a property of the car, and not specifically about the association between the Driver and the Car. If Mileage was defined as the total number of miles that car was driven by that driver, then it would be suitable as an association class.
[W7.2] Sequence Diagrams: Intermediate-Level
Can draw intermediate-level sequence diagrams
What’s going on here?
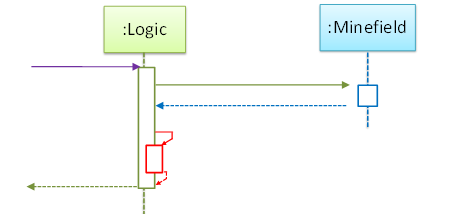
- a.
Logicobject is executing a parallel thread. - b.
Logicobject is executing a loop. - c.
Logicobject is creating anotherLogicinstance. - d. One of
Logicobject’s methods is calling another of its methods. - e.
Minefieldobject is calling a method ofLogic.
(d)
Explain the interactions depicted in this sequence diagram.
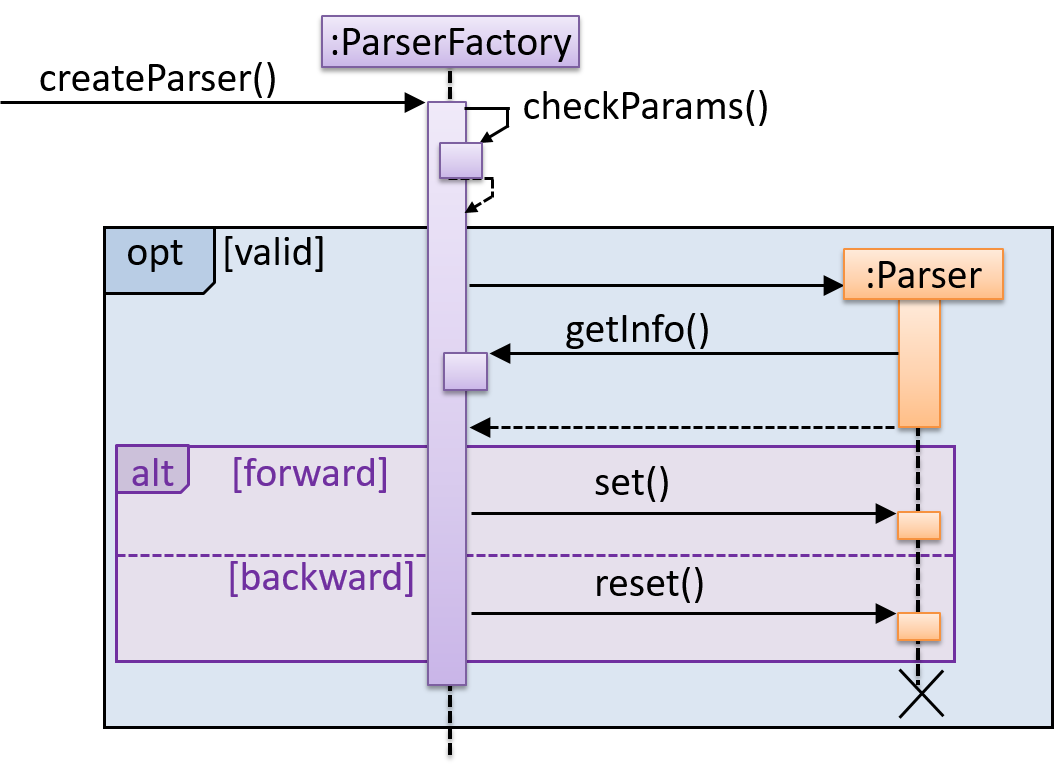
First, the createParser() method of an existing ParserFactory object is called. Then, ...
Draw a sequence diagram to represent this code snippet.
if (isFirstPage) {
new Quote().print();
}
The Quote class:
class Quote{
String q;
Quote(){
q = generate();
}
String generate(){
// ...
}
void print(){
System.out.println(q);
}
}
- Show
new Quote().print();as two method calls. - As the created Quote object is not assigned to a variable, it can be considered as 'deleted' soon after its
print()method is called.
Can interpret sequence diagrams with reference frames
UML uses ref frame to allow a segment of the interaction to be omitted and shown as a separate sequence diagram. Reference frames help us to break complicated sequence diagrams into multiple parts or simply to omit details we are not interested in showing.
Notation:

The details of the get minefield appearance interactions have been omitted from the diagram.
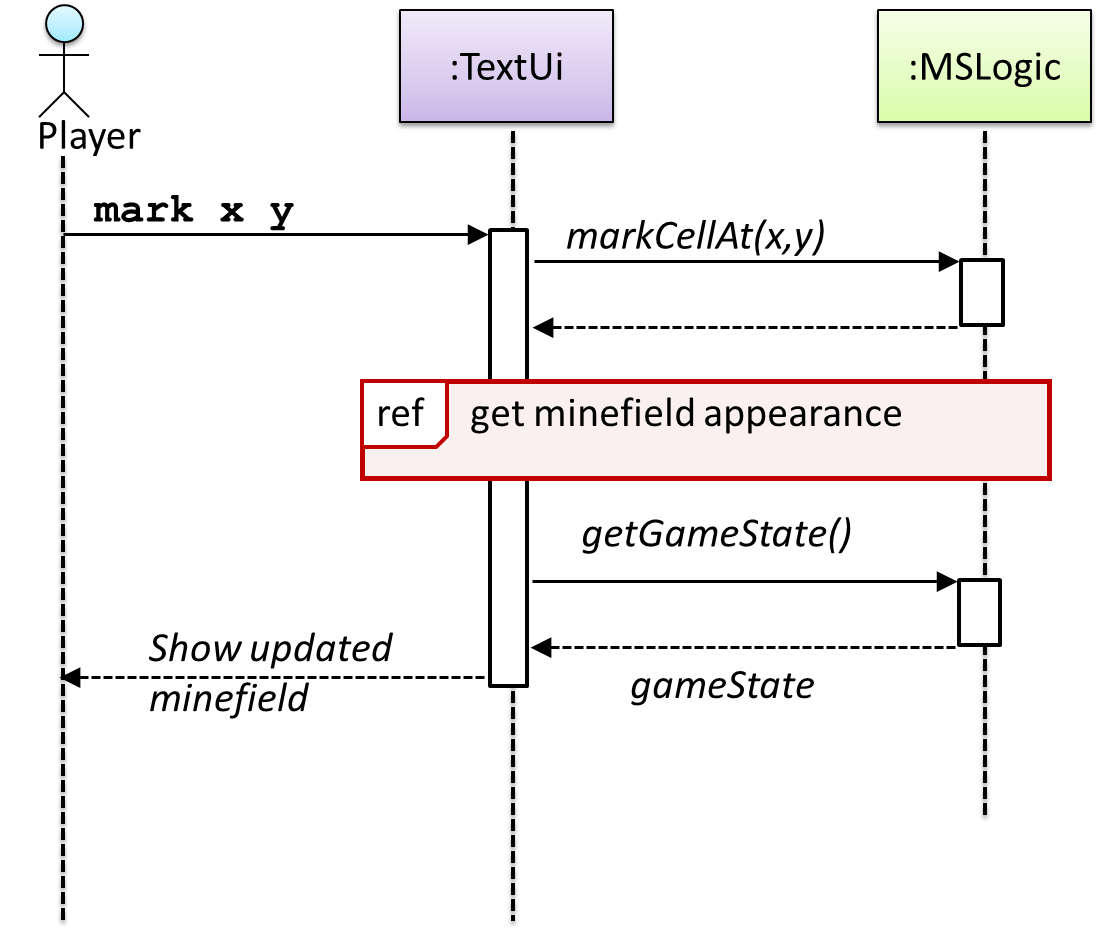
Those details are shown in a separate sequence diagram given below.
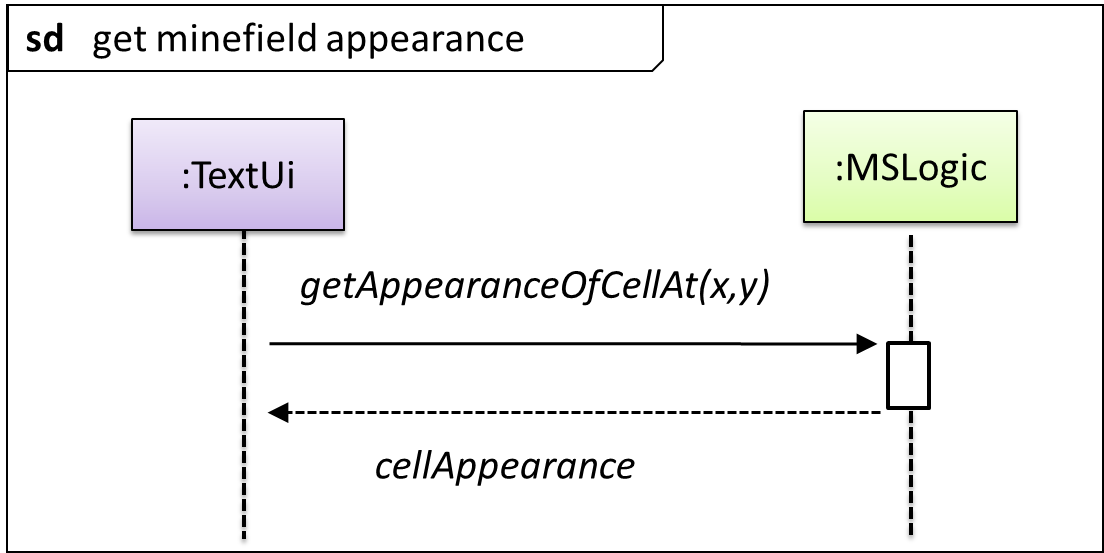
Can interpret sequence diagrams with parallel paths
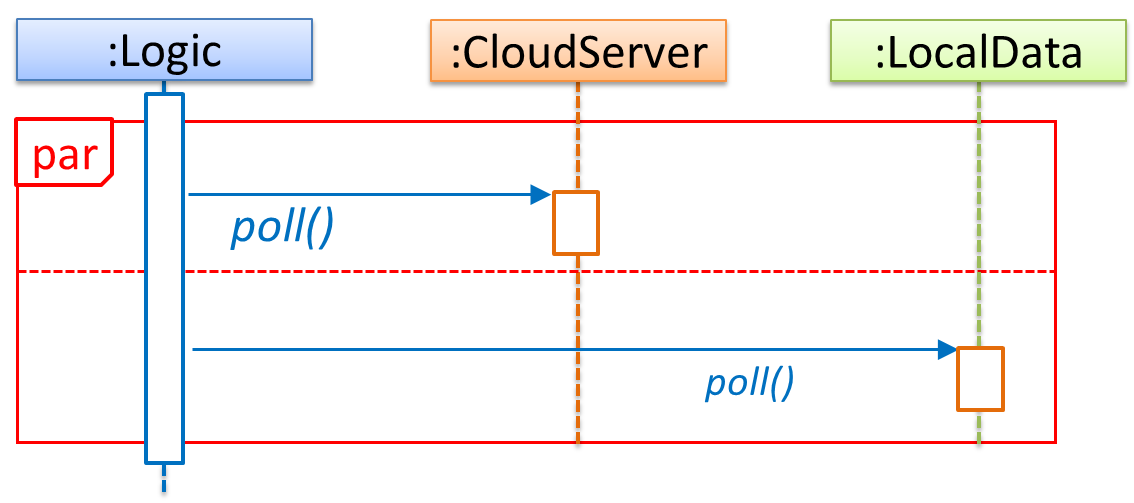
UML uses par frames to indicate parallel paths.
Notation:

Logic is calling methods CloudServer#poll() and LocalServer#poll() in parallel.
💡 If you show parallel paths in a sequence diagram, the corresponding Java implementation is likely to be multi-threaded because a normal Java program cannot do multiple things at the same time.
[W7.3] Architectural Styles
Can explain architectural styles
Software architectures follow various high-level styles (aka architectural patterns), just like
n-tier style, client-server style, event-driven style, transaction processing style, service-oriented style, pipes-and-filters style, message-driven style, broker style, ...
source: https://inspectapedia.com
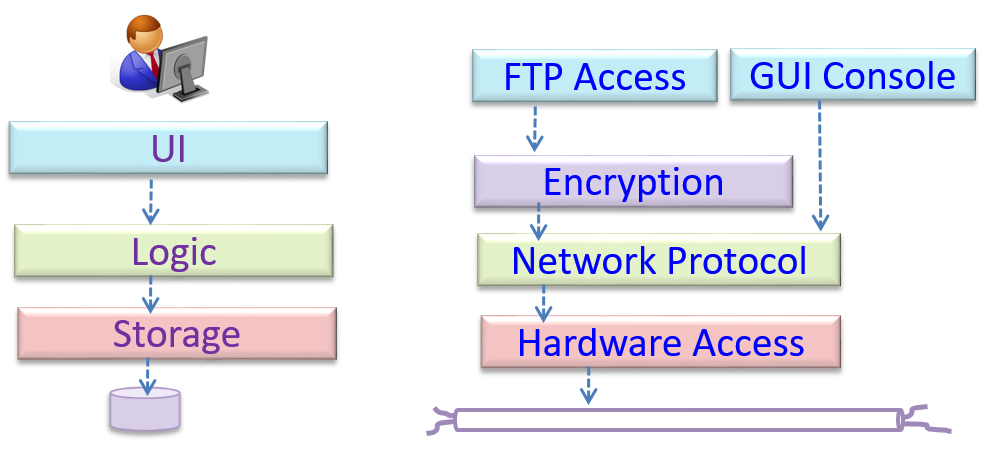
Can identify n-tier architectural style
In the n-tier style, higher layers make use of services provided by lower layers. Lower layers are independent of higher layers. Other names: multi-layered, layered.
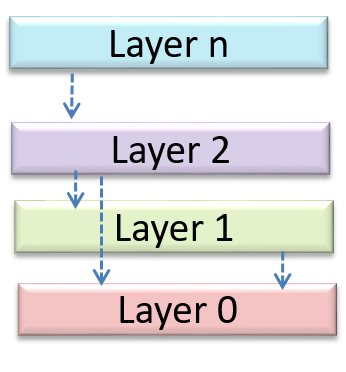
Operating systems and network communication software often use n-tier style.
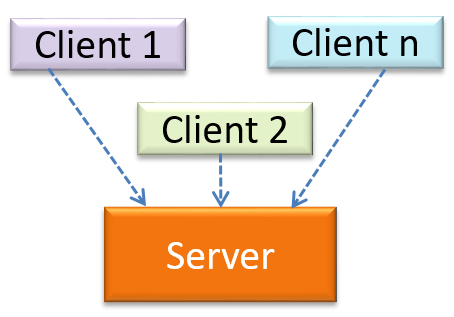
Can identify the client-server architectural style
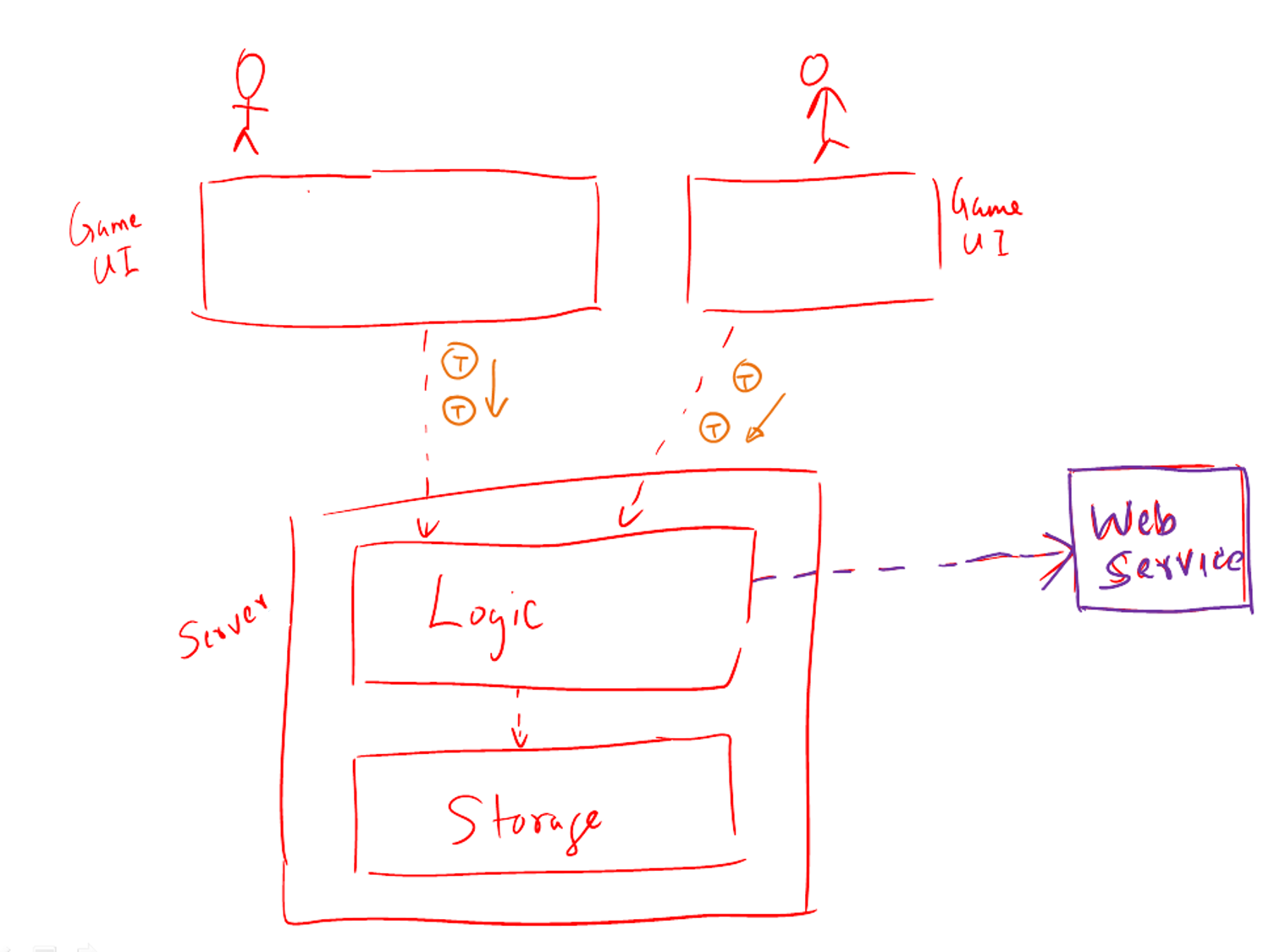
The client-server style has at least one component playing the role of a server and at least one client component accessing the services of the server. This is an architectural style used often in distributed applications.
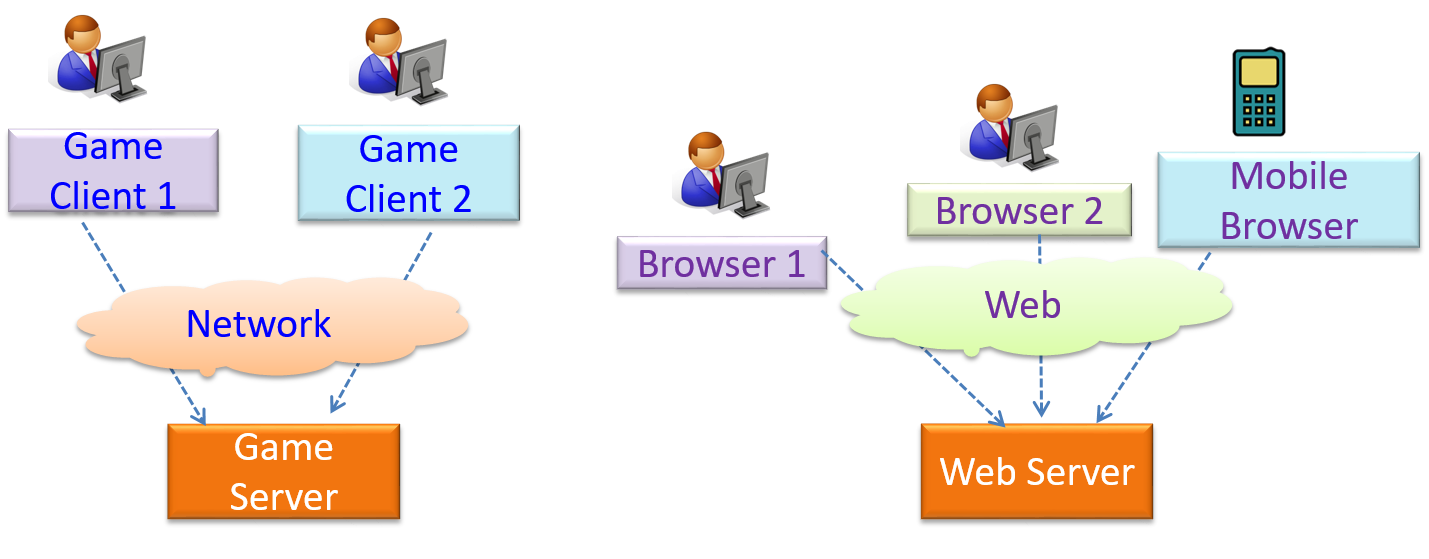
The online game and the Web application below uses the client-server style.
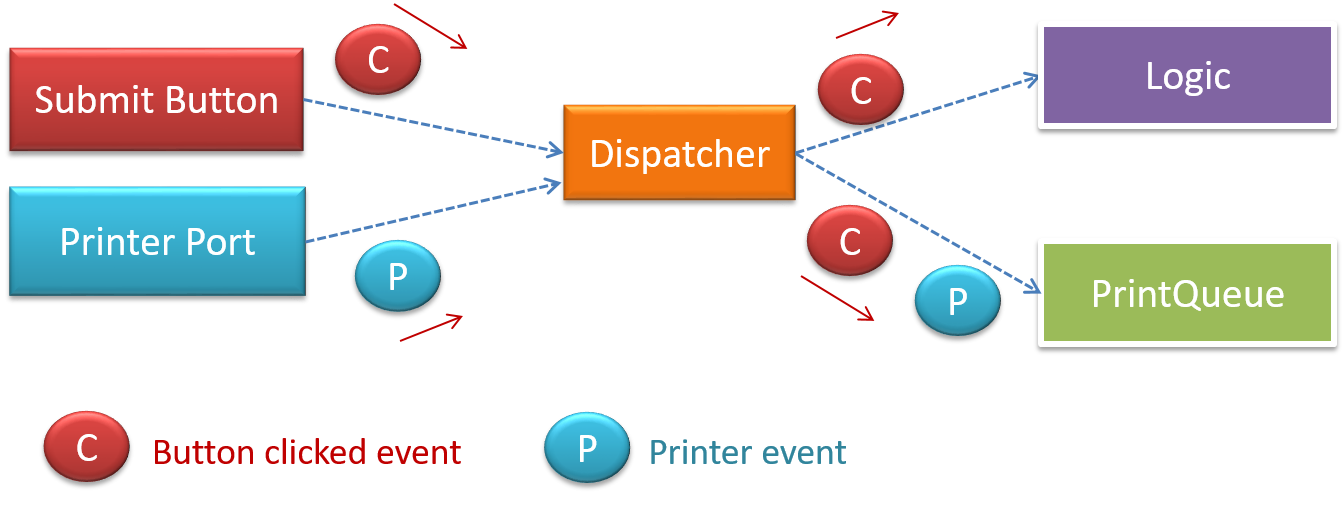
Can identify event-driven architectural style
Event-driven style controls the flow of the application by detecting
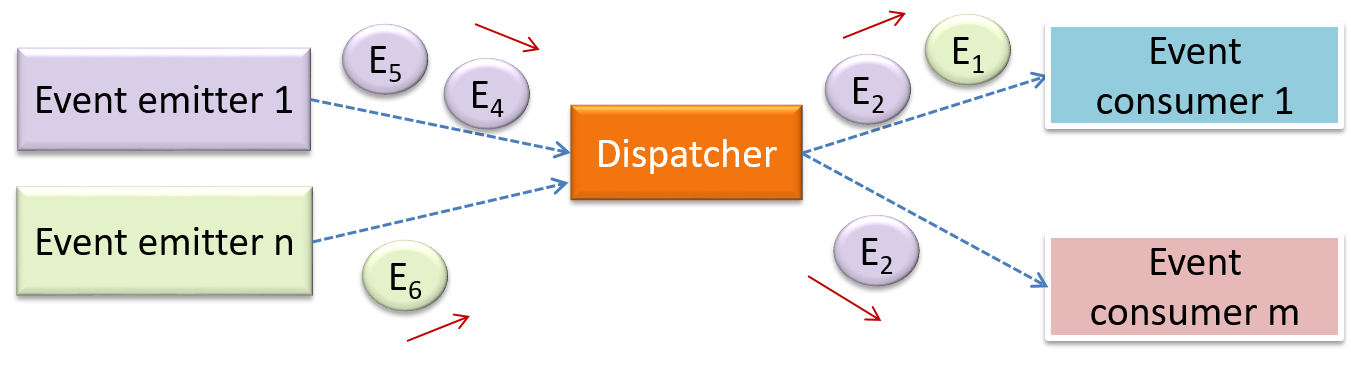
When the ‘button clicked’ event occurs in a GUI, that event can be transmitted to components that are interested in reacting to that event. Similarly, events detected at a Printer port can be transmitted to components related to operating the Printer. The same event can be sent to multiple consumers too.
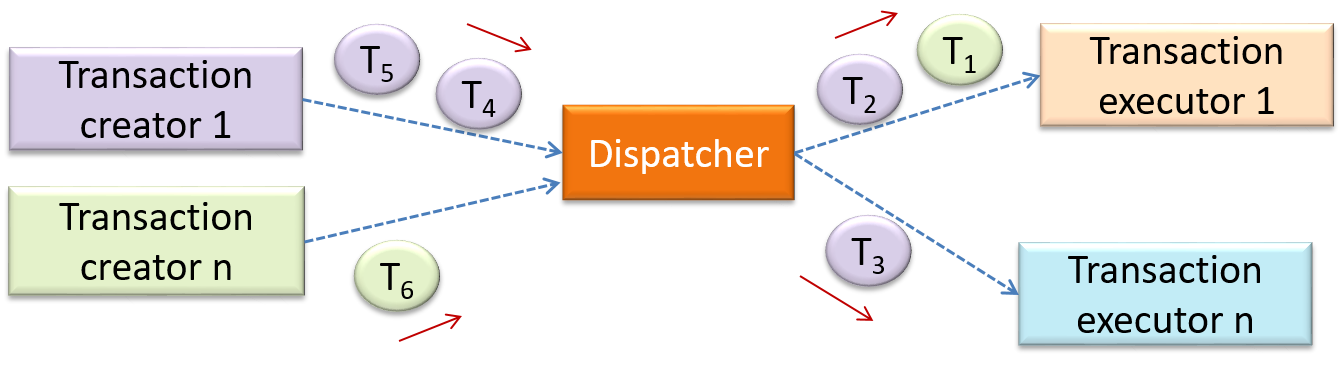
Can identify transaction processing architectural style
The transaction processing style divides the workload of the system down to a number of transactions which are then given to a dispatcher that controls the execution of each transaction. Task queuing, ordering, undo etc. are handled by the dispatcher.
In this example from a Banking system, transactions are generated by the terminals used by
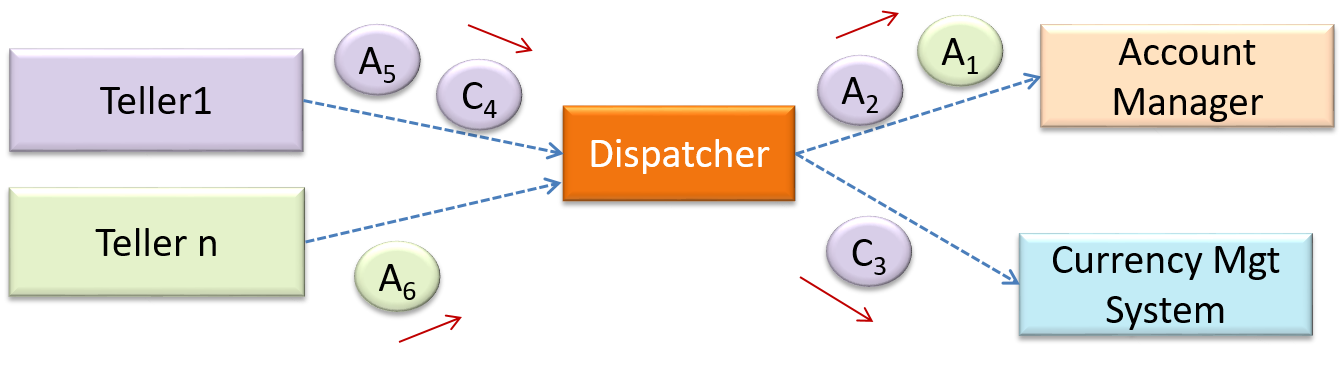
Can identify service-oriented architectural style
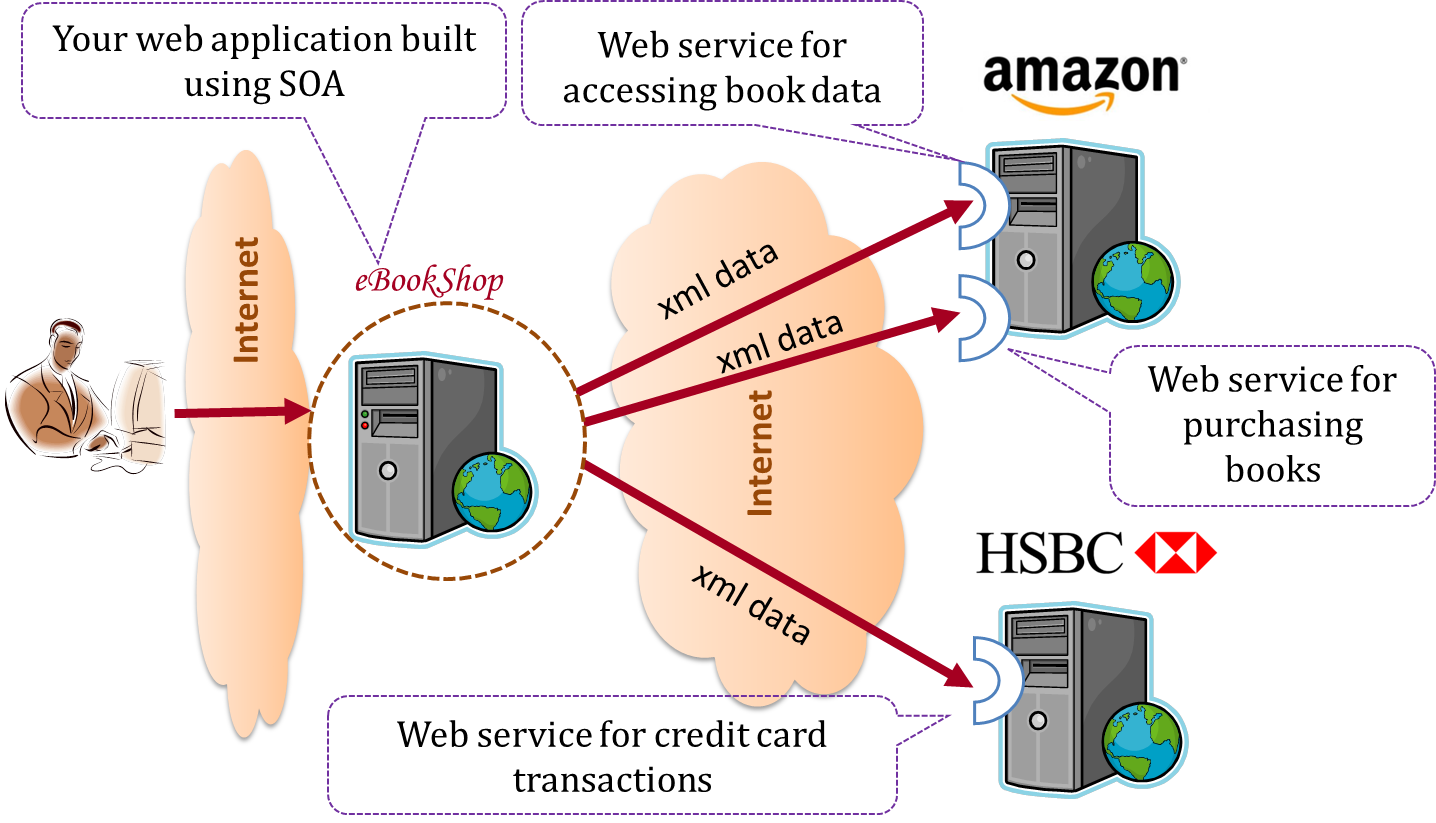
The service-oriented architecture (SOA) style builds applications by combining functionalities packaged as programmatically accessible services. SOA aims to achieve interoperability between distributed services, which may not even be implemented using the same programming language. A common way to implement SOA is through the use of XML web services where the web is used as the medium for the services to interact, and XML is used as the language of communication between service providers and service users.
Suppose that Amazon.com provides a web service for customers to browse and buy merchandise, while HSBC provides a web service for merchants to charge HSBC credit cards. Using these web services, an ‘eBookShop’ web application can be developed that allows HSBC customers to buy merchandise from Amazon and pay for them using HSBC credit cards. Because both Amazon and HSBC services follow the SOA architecture, their web services can be reused by the web application, even if all three systems use different programming platforms.
Can name several other architecture styles
Other well-known architectural styles include the pipes-and-filters architectures, the broker architectures, the peer-to-peer architectures, and the message-oriented architectures.
-
Pipes and Filters pattern -- an article from Microsoft about the pipes and filters architectural style
-
Broker pattern -- Wikipedia article on the broker architectural style
-
Peer-to-peer pattern -- Wikipedia article on the P2P architectural style
-
Message-driven processing -- a post by Margaret Rouse
Can explain how architectural styles are combined
Most applications use a mix of these architectural styles.
An application can use a client-server architecture where the server component comprises several layers, i.e. it uses the n-Tier architecture.
Assume you are designing a multiplayer version of the Minesweeper game where any number of players can play the same Minefield. Players use their own PCs to play the game. A player scores by deducing a cell correctly before any of the other players do. Once a cell is correctly deduced, it appears as either marked or cleared for all players.
Comment on how each of the following architectural styles could be potentially useful when designing the architecture for this game.
- Client-server
- Transaction-processing
- SOA (Service Oriented Architecture)
- multi-layer (n-tier)
- Client-server – Clients can be the game UI running on player PCs. The server can be the game logic running on one machine.
- Transaction-processing – Each player action can be packaged as transactions (by the client component running on the player PC) and sent to the server. Server processes them in the order they are received.
- SOA – The game can access a remote web services for things such as getting new puzzles, validating puzzles, charging players subscription fees, etc.
- Multi-layer – The server component can have two layers: logic layer and the storage layer.
[W7.4] APIs
Can explain APIs
An Application Programming Interface (API) specifies the interface through which other programs can interact with a software component. It is a contract between the component and its clients.
A class has an API (e.g., API of the Java String class, API of the Python str class) which is a collection of public methods that you can invoke to make use of the class.
The GitHub API is a collection of Web request formats GitHub server accepts and the corresponding responses. We can write a program that interacts with GitHub through that API.
When developing large systems, if you define the API of each components early, the development team can develop the components in parallel because the future behavior of the other components are now more predictable.
Choose the correct statements
- a. A software component can have an API.
- b. Any method of a class is part of its API.
- c. Private methods of a class are not part of its API.
- d. The API forms the contract between the component developer and the component user.
- e. Sequence diagrams can be used to show how components interact with each other via APIs.
(a) (c) (d) (e)
Explanation: (b) is incorrect because private methods cannot be a part of the API
Defining component APIs early is useful for developing components in parallel.
True
Explanation: Yes, once we know the precise behavior expected of each component, we can start developing them in parallel.
[W7.5] Basic Design Approaches
Can explain top-down and bottom-up design
Multi-level design can be done in a top-down manner, bottom-up manner, or as a mix.
- Top-down: Design the high-level design first and flesh out the lower levels later. This is especially useful when designing big and novel systems where the high-level design needs to be stable before lower levels can be designed.
- Bottom-up: Design lower level components first and put them together to create the higher-level systems later. This is not usually scalable for bigger systems. One instance where this approach might work is when designing a variations of an existing system or re-purposing existing components to build a new system.
- Mix: Design the top levels using the top-down approach but switch to a bottom-up approach when designing the bottom levels.
Top-down design is better than bottom-up design.
False
Explanation: Not necessarily. It depends on the situation. Bottom-up design may be preferable when there are lot of existing components we want to reuse.
Can explain agile design
Agile design can be contrasted with full upfront design in the following way:
Agile designs are emergent, they’re not defined up front. Your overall system design will emerge over time, evolving to fulfill new requirements and take advantage of new technologies as appropriate. Although you will often do some initial architectural modeling at the very beginning of a project, this will be just enough to get your team going. This approach does not produce a fully documented set of models in place before you may begin coding. -- adapted from agilemodeling.com
Agile design camp expects the design to change over the product’s lifetime.
True
Explanation: Yes, that is why they do not believe in spending too much time creating a detailed and full design at the very beginning. However, the architecture is expected to remain relatively stable even in the agile design approach.
[W7.6] Project Mgt: Scheduling and Tracking
Can explain milestones
A milestone is the end of a stage which indicates a significant progress. We should take into account dependencies and priorities when deciding on the features to be delivered at a certain milestone.
Each intermediate product release is a milestone.
In some projects, it is not practical to have a very detailed plan for the whole project due to the uncertainty and unavailability of required information. In such cases, we can use a high-level plan for the whole project and a detailed plan for the next few milestones.
Milestones for the Minesweeper project, iteration 1
| Day | Milestones |
|---|---|
| Day 1 | Architecture skeleton completed |
| Day 3 | ‘new game’ feature implemented |
| Day 4 | ‘new game’ feature tested |
Can explain buffers
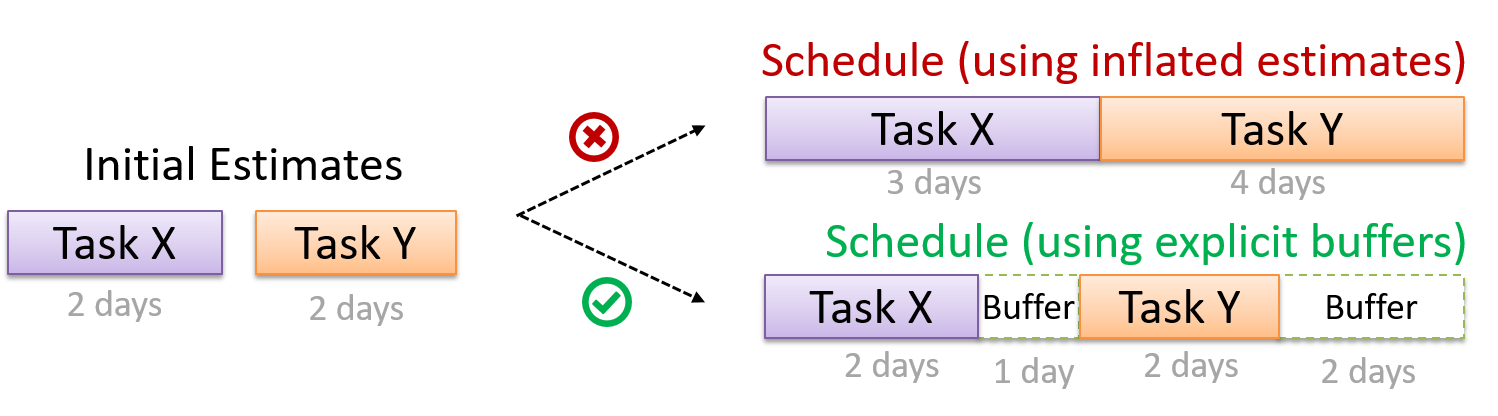
A buffer is a time set aside to absorb any unforeseen delays. It is very important to include buffers in a software project schedule because effort/time estimations for software development is notoriously hard. However, do not inflate task estimates to create hidden buffers; have explicit buffers instead. Reason: With explicit buffers it is easier to detect incorrect effort estimates which can serve as a feedback to improve future effort estimates.
Can explain issue trackers
Keeping track of project tasks (who is doing what, which tasks are ongoing, which tasks are done etc.) is an essential part of project management. In small projects it may be possible to track tasks using simple tools as online spreadsheets or general-purpose/light-weight tasks tracking tools such as Trello. Bigger projects need more sophisticated task tracking tools.
Issue trackers (sometimes called bug trackers) are commonly used to track task assignment and progress. Most online project management software such as GitHub, SourceForge, and BitBucket come with an integrated issue tracker.
A screenshot from the Jira Issue tracker software (Jira is part of the BitBucket project management tool suite):
Can explain work breakdown structures
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) depicts information about tasks and their details in terms of subtasks. When managing projects it is useful to divide the total work into smaller, well-defined units. Relatively complex tasks can be further split into subtasks. In complex projects a WBS can also include prerequisite tasks and effort estimates for each task.
The high level tasks for a single iteration of a small project could look like the following:
| Task ID | Task | Estimated Effort | Prerequisite Task |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Analysis | 1 man day | - |
| B | Design | 2 man day | A |
| C | Implementation | 4.5 man day | B |
| D | Testing | 1 man day | C |
| E | Planning for next version | 1 man day | D |
The effort is traditionally measured in man hour/day/month i.e. work that can be done by one person in one hour/day/month. The Task ID is a label for easy reference to a task. Simple labeling is suitable for a small project, while a more informative labeling system can be adopted for bigger projects.
An example WBS for a project for developing a game.
| Task ID | Task | Estimated Effort | Prerequisite Task |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | High level design | 1 man day | - |
| B |
Detail design
|
2 man day
|
A |
| C |
Implementation
|
4.5 man day
|
|
| D | System Testing | 1 man day | C |
| E | Planning for next version | 1 man day | D |
All tasks should be well-defined. In particular, it should be clear as to when the task will be considered done.
Some examples of ill-defined tasks and their better-defined counterparts:
| Bad | Better |
|---|---|
| more coding | implement component X |
| do research on UI testing | find a suitable tool for testing the UI |
Which one these project tasks is not well-defined?
(c)
Explanation: ‘More testing’ is not well-defined. How much is ‘more’? ‘Test the delete functionality’ is a better-defined task.
Can explain GANTT charts
A Gantt chart is a 2-D bar-chart, drawn as time vs tasks (represented by horizontal bars).
A sample Gantt chart:
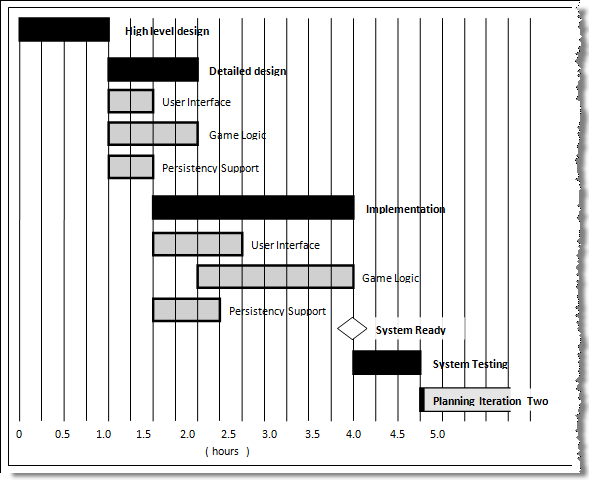
In a Gantt chart, a solid bar represents the main task, which is generally composed of a number of subtasks, shown as grey bars. The diamond shape indicates an important deadline/deliverable/milestone.
Can explain PERT charts
PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique) chart uses a graphical technique to show the order/sequence of tasks. It is based on a simple idea of drawing a directed graph in which:
- Node or vertex captures the effort estimation of a task, and
- Arrow depicts the precedence between tasks
an example PERT chart for a simple software project
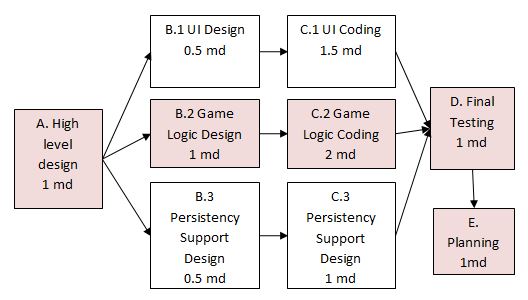
md = man days
A PERT chart can help determine the following important information:
- The order of tasks. In the example above,
Final Testingcannot begin until all coding of individual subsystems have been completed. - Which tasks can be done concurrently. In the example above, the various subsystem designs can start independently once the
High level designis completed. - The shortest possible completion time. In the example above, there is a path (indicated by the shaded boxes) from start to end that determines the shortest possible completion time.
- The Critical Path. In the example above, the shortest possible path is also the critical path.
Critical path is the path in which any delay can directly affect the project duration. It is important to ensure tasks on the critical path are completed on time.
Can explain common team structures
Given below are three commonly used team structures in software development. Irrespective of the team structure, it is a good practice to assign roles and responsibilities to different team members so that someone is clearly in charge of each aspect of the project. In comparison, the ‘everybody is responsible for everything’ approach can result in more chaos and hence slower progress.
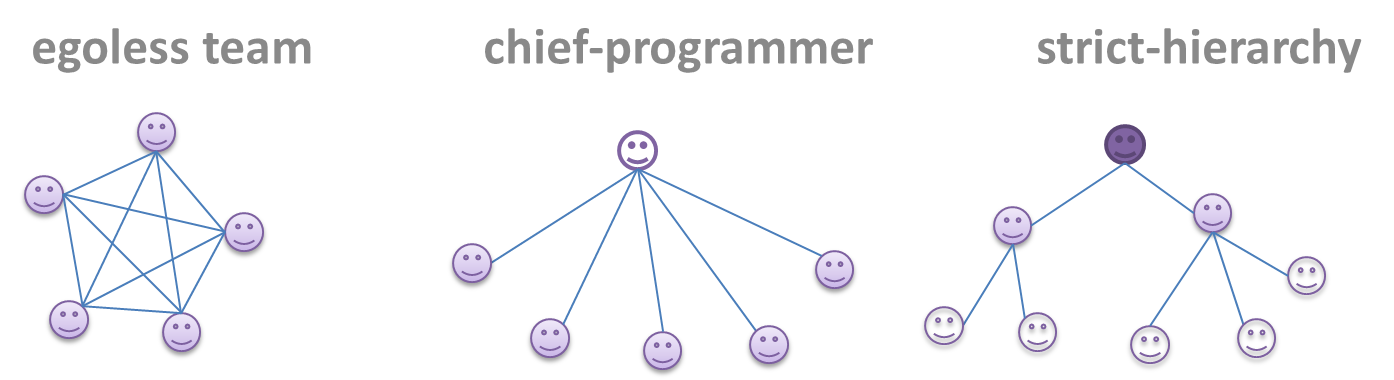
Egoless team
In this structure, every team member is equal in terms of responsibility and accountability. When any decision is required, consensus must be reached. This team structure is also known as a democratic team structure. This team structure usually finds a good solution to a relatively hard problem as all team members contribute ideas.
However, the democratic nature of the team structure bears a higher risk of falling apart due to the absence of an authority figure to manage the team and resolve conflicts.
Chief programmer team
Frederick Brooks proposed that software engineers learn from the medical surgical team in an operating room. In such a team, there is always a chief surgeon, assisted by experts in other areas. Similarly, in a chief programmer team structure, there is a single authoritative figure, the chief programmer. Major decisions, e.g. system architecture, are made solely by him/her and obeyed by all other team members. The chief programmer directs and coordinates the effort of other team members. When necessary, the chief will be assisted by domain specialists e.g. business specialists, database expert, network technology expert, etc. This allows individual group members to concentrate solely on the areas where they have sound knowledge and expertise.
The success of such a team structure relies heavily on the chief programmer. Not only must he be a superb technical hand, he also needs good managerial skills. Under a suitably qualified leader, such a team structure is known to produce successful work. .
Strict hierarchy team
In the opposite extreme of an egoless team, a strict hierarchy team has a strictly defined organization among the team members, reminiscent of the military or bureaucratic government. Each team member only works on his assigned tasks and reports to a single “boss”.
In a large, resource-intensive, complex project, this could be a good team structure to reduce communication overhead.
Which team structure is the most suitable for a school project?
(a)
Explanation: Given that students are all peers and beginners, Egoless team structure seems most suitable for a school project. However, given school projects are low-stakes, short-lived, and small, even the other two team structures can be used for them.
Project Milestone: v1.1
Update UG in the repo, attempt to do global-impact changes to the code base.
Milestone progress is graded. Be reminded that reaching individual and team milestones are considered for
Most aspects project progress are tracked using automated scripts. Please follow our instructions closely or else the script will not be able to detect your progress. We prefer not to spend admin resources processing requests for partial credit for work that did not follow the instructions precisely, unless the progress was not detected due to a bug in the script.
Milestone requirements are cumulative. The recommended progress for the mid-milestone is an implicit requirement for the actual milestone unless a milestone requirement overrides a mid-milestone requirement e.g., mid-milestone requires a document to be in a temp format while the actual milestone requires it to be in the proper format. Similarly, a requirement for milestone n is also an implicit requirement for milestone n+1 unless n+1 overrides the n requirement. This means if you miss some requirement at milestone n, you should try to achieve it before milestone n+1 or else it could be noted again as a 'missed requirement' at milestone n+1.
v1.1 Summary of Milestone
| Milestone | Minimum acceptable performance to consider as 'reached' |
|---|---|
| Team org/repo set up | as stated in |
| Some code enhancements done | created PRs to do local/global changes |
| Photo uploaded | a photo complying to |
| Project docs updated | updated docs are merged to the master branch |
| Milestone wrapped up | a commit in the master branch tagged as v1.1 |
Set up project repo, start moving UG and DG to the repo, attempt to do local-impact changes to the code base.
Project Management:
Set up the team org and the team repo as explained below:
Relevant: [
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Relevant: [
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
When updating code in the repo, follow the workflow explained below:
Relevant: [
Workflow
Before you do any coding for the project,
- Ensure you have
set the Git username correctly (as explained in Appendix E) in all Computers you use for coding. - Read
our reuse policy (in Admin: Appendix B) , in particular, how to give credit when you reuse code from the Internet or classmates:
Setting Git Username to Match GitHub Username
We use various tools to analyze your code. For us to be able to identify your commits, you should use the GitHub username as your Git username as well. If there is a mismatch, or if you use multiple user names for Git, our tools might miss some of your work and as a result you might not get credit for some of your work.
In each Computer you use for coding, after installing Git, you should set the Git username as follows.
- Open a command window that can run Git commands (e.g., Git bash window)
- Run the command
git config --global user.name YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME
e.g.,git config --global user.name JohnDoe
More info about setting Git username is here.
Policy on reuse
Reuse is encouraged. However, note that reuse has its own costs (such as the learning curve, additional complexity, usage restrictions, and unknown bugs). Furthermore, you will not be given credit for work done by others. Rather, you will be given credit for using work done by others.
- You are allowed to reuse work from your classmates, subject to following conditions:
- The work has been published by us or the authors.
- You clearly give credit to the original author(s).
- You are allowed to reuse work from external sources, subject to following conditions:
- The work comes from a source of 'good standing' (such as an established open source project). This means you cannot reuse code written by an outside 'friend'.
- You clearly give credit to the original author. Acknowledge use of third party resources clearly e.g. in the welcome message, splash screen (if any) or under the 'about' menu. If you are open about reuse, you are less likely to get into trouble if you unintentionally reused something copyrighted.
- You do not violate the license under which the work has been released. Please do not use 3rd-party images/audio in your software unless they have been specifically released to be used freely. Just because you found it in the Internet does not mean it is free for reuse.
- Always get permission from us before you reuse third-party libraries. Please post your 'request to use 3rd party library' in our forum. That way, the whole class get to see what libraries are being used by others.
Giving credit for reused work
Given below are how to give credit for things you reuse from elsewhere. These requirements are specific to this module i.e., not applicable outside the module (outside the module you should follow the rules specified by your employer and the license of the reused work)
If you used a third party library:
- Mention in the
README.adoc(under the Acknowledgements section) - mention in the
Project Portfolio Page if the library has a significant relevance to the features you implemented
If you reused code snippets found on the Internet e.g. from StackOverflow answers or
referred code in another software or
referred project code by current/past student:
- If you read the code to understand the approach and implemented it yourself, mention it as a comment
Example://Solution below adapted from https://stackoverflow.com/a/16252290 {Your implmentation of the reused solution here ...} - If you copy-pasted a non-trivial code block (possibly with minor modifications renaming, layout changes, changes to comments, etc.), also mark the code block as reused code (using
@@authortags
Format://@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused //{Info about the source...} {Reused code (possibly with minor modifications) here ...} //@@authorpersons = getList() //@@author johndoe-reused //Reused from https://stackoverflow.com/a/34646172 with minor modifications Collections.sort(persons, new Comparator<CustomData>() { @Override public int compare(CustomData lhs, CustomData rhs) { return lhs.customInt > rhs.customInt ? -1 : (lhs.customInt < rhs.customInt) ? 1 : 0; } }); //@@author return persons;
Adding @@author tags indicate authorship
-
Mark your code with a
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}. Note the double@.
The//@@authortag should indicates the beginning of the code you wrote. The code up to the next//@@authortag or the end of the file (whichever comes first) will be considered as was written by that author. Here is a sample code file://@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author sarahkhoo method 3 ... //@@author johndoe method 4 ... -
If you don't know who wrote the code segment below yours, you may put an empty
//@@author(i.e. no GitHub username) to indicate the end of the code segment you wrote. The author of code below yours can add the GitHub username to the empty tag later. Here is a sample code with an emptyauthortag:method 0 ... //@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author method 3 ... method 4 ... -
The author tag syntax varies based on file type e.g. for java, css, fxml. Use the corresponding comment syntax for non-Java files.
Here is an example code from an xml/fxml file.<!-- @@author sereneWong --> <textbox> <label>...</label> <input>...</input> </textbox> ... -
Do not put the
//@@authorinside java header comments.
👎/** * Returns true if ... * @@author johndoe */👍
//@@author johndoe /** * Returns true if ... */
What to and what not to annotate
-
Annotate both functional and test code There is no need to annotate documentation files.
-
Annotate only significant size code blocks that can be reviewed on its own e.g., a class, a sequence of methods, a method.
Claiming credit for code blocks smaller than a method is discouraged but allowed. If you do, do it sparingly and only claim meaningful blocks of code such as a block of statements, a loop, or an if-else statement.- If an enhancement required you to do tiny changes in many places, there is no need to annotate all those tiny changes; you can describe those changes in the Project Portfolio page instead.
- If a code block was touched by more than one person, either let the person who wrote most of it (e.g. more than 80%) take credit for the entire block, or leave it as 'unclaimed' (i.e., no author tags).
- Related to the above point, if you claim a code block as your own, more than 80% of the code in that block should have been written by yourself. For example, no more than 20% of it can be code you reused from somewhere.
- 💡 GitHub has a blame feature and a history feature that can help you determine who wrote a piece of code.
-
Do not try to boost the quantity of your contribution using unethical means such as duplicating the same code in multiple places. In particular, do not copy-paste test cases to create redundant tests. Even repetitive code blocks within test methods should be extracted out as utility methods to reduce code duplication. Individual members are responsible for making sure code attributed to them are correct. If you notice a team member claiming credit for code that he/she did not write or use other questionable tactics, you can email us (after the final submission) to let us know.
-
If you wrote a significant amount of code that was not used in the final product,
- Create a folder called
{project root}/unused - Move unused files (or copies of files containing unused code) to that folder
- use
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-unusedto mark unused code in those files (note the suffixunused) e.g.
//@@author johndoe-unused method 1 ... method 2 ...Please put a comment in the code to explain why it was not used.
- Create a folder called
-
If you reused code from elsewhere, mark such code as
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused(note the suffixreused) e.g.//@@author johndoe-reused method 1 ... method 2 ... -
You can use empty
@@authortags to mark code as not yours when RepoSense attribute the to you incorrectly.-
Code generated by the IDE/framework, should not be annotated as your own.
-
Code you modified in minor ways e.g. adding a parameter. These should not be claimed as yours but you can mention these additional contributions in the Project Portfolio page if you want to claim credit for them.
-
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Features implemented: A summary of the features you implemented. If you implemented multiple features, you are recommended to indicate which one is the biggest feature.
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP
-
-
Page limit:
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 (soft limit) Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 (soft limit) Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 (soft limit) Total 5-10 (strict) - The page limits given above are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
- Reason for page limit: These submissions are peer-graded (in the PE) which needs to be done in a limited time span.
If you have more content than the limit given above, you can give a representative samples of UG and DG that showcase your documentation skills. Those samples should be understandable on their own. For the parts left-out, you can give an abbreviated version and refer the reader to the full UG/DG for more details.
It's similar to giving extra details as appendices; the reader will look at the UG/DG if the PPP is not enough to make a judgment. For example, when judging documentation quality, if the part in the PPP is not well-written, there is no point reading the rest in the main UG/DG. That's why you need to put the most representative part of your writings in the PPP and still give an abbreviated version of the rest in the PPP itself. Even when judging the quantity of work, the reader should be able to get a good sense of the quantity by combining what is quoted in the PPP and your abbreviated description of the missing part. There is no guarantee that the evaluator will read the full document.
Follow the
- Get team members to review PRs. A workflow without PR reviews is a risky workflow.
- Do not merge PRs failing
CI . After setting up Travis, the CI status of a PR is reported at the bottom of the PR page. The screenshot below shows the status of a PR that is passing all CI checks.
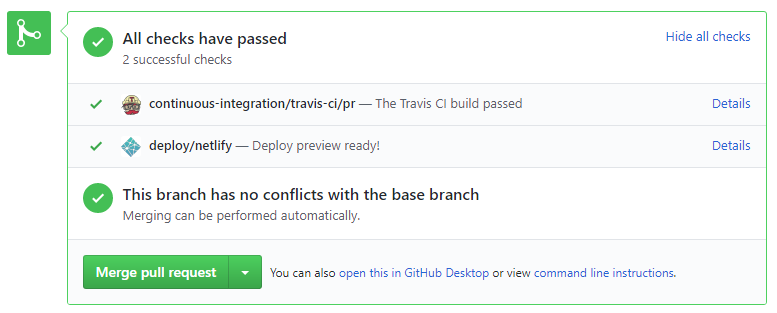
If there is a failure, you can click on theDetailslink in corresponding line to find out more about the failure. Once you figure out the cause of the failure, push the a fix to the PR. - After setting up Netlify, you can use Netlify PR Preview to preview changes to documentation files, if the PR contains updates to documentation. To see the preview, click on the
Detailslink in front of the Netlify status reported (refer screenshot above).
After completing v1.1, you can adjust process rigor to suit your team's pace, as explained below.
-
Reduce automated tests have benefits, but they can be a pain to write/maintain; GUI tests are especially hard to maintain because their behavior can sometimes depend on things such as the OS, resolution etc.
It is OK to get rid of some of the troublesome tests and rely more on manual testing instead. The less automated tests you have, the higher the risk of regressions; but it may be an acceptable trade-off under the circumstances if tests are slowing you down too much.
There is no direct penalty for removing GUI tests. Also noteour expectation on test code . -
Reduce automated checks: You can also reduce the rigor of checkstyle checks to expedite PR processing.
-
Switch to a lighter workflow: While forking workflow is the safest, it is also rather heavy. You an switch to a simpler workflow if the forking workflow is slowing you down. Refer the textbook to find more about alternative workflows: branching workflow, centralized workflow. However, we still recommend that you use PR reviews, at least for PRs affecting others' features.
You can also increase the rigor/safety of your workflow in the following ways:
- Use GitHub's Protected Branches feature to protect your
masterbranch against rogue PRs.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
Project Management → Revision Control →
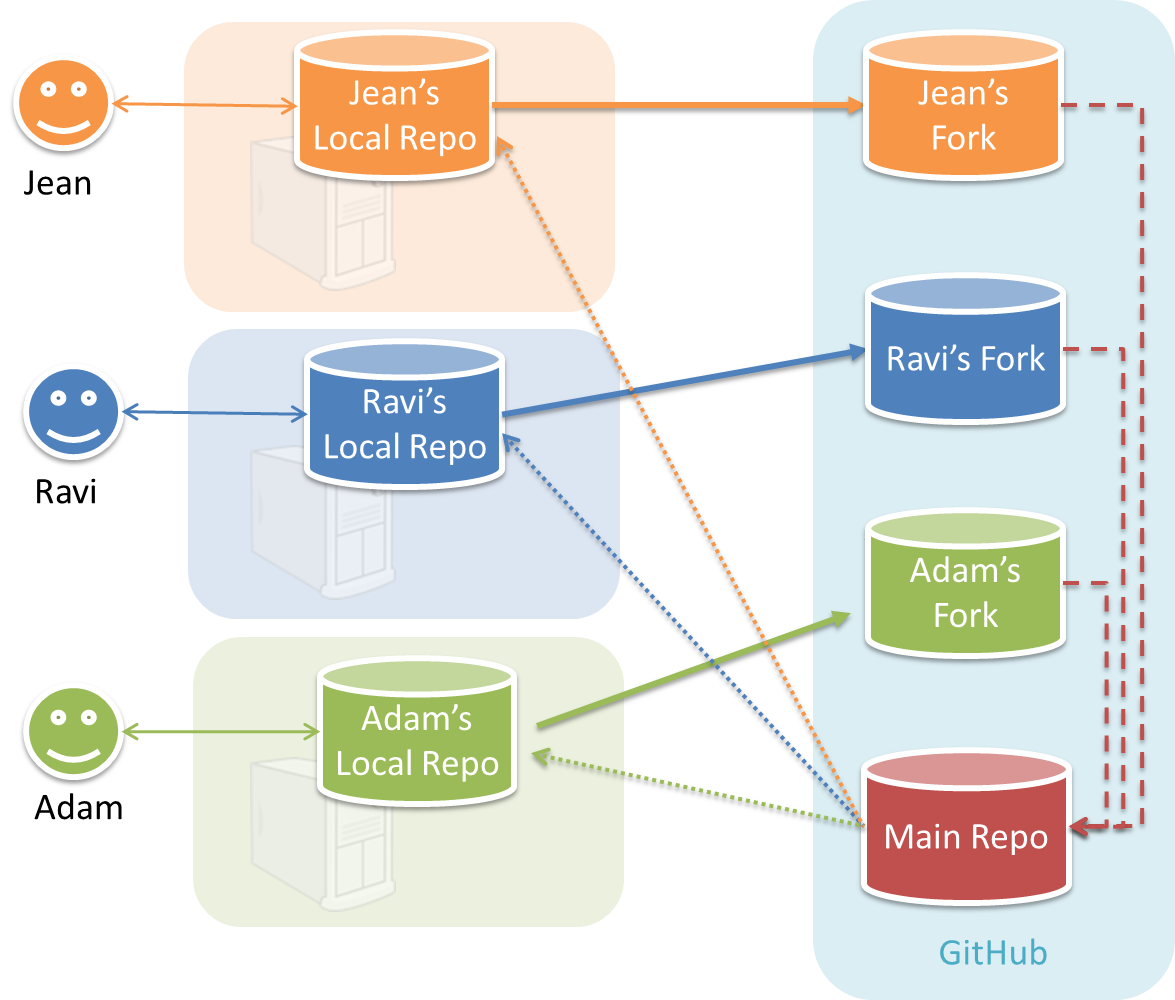
In the forking workflow, the 'official' version of the software is kept in a remote repo designated as the 'main repo'. All team members fork the main repo create pull requests from their fork to the main repo.
To illustrate how the workflow goes, let’s assume Jean wants to fix a bug in the code. Here are the steps:
- Jean creates a separate branch in her local repo and fixes the bug in that branch.
- Jean pushes the branch to her fork.
- Jean creates a pull request from that branch in her fork to the main repo.
- Other members review Jean’s pull request.
- If reviewers suggested any changes, Jean updates the PR accordingly.
- When reviewers are satisfied with the PR, one of the members (usually the team lead or a designated 'maintainer' of the main repo) merges the PR, which brings Jean’s code to the main repo.
- Other members, realizing there is new code in the upstream repo, sync their forks with the new upstream repo (i.e. the main repo). This is done by pulling the new code to their own local repo and pushing the updated code to their own fork.
- A detailed explanation of the Forking Workflow - From Atlassian
Documentation:
Recommended procedure for updating docs:
- Divide among yourselves who will update which parts of the document(s).
- Update the team repo by following the workflow mentioned above.
Update the following pages in your project repo:
- About Us page:
This page is used for module admin purposes. Please follow the format closely or else our scripts will not be able to give credit for your work.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
here . - Including the name/photo of the supervisor/lecturer is optional.
- The photo of a team member should be
doc/images/githbub_username_in_lower_case.pnge.g.docs/images/damithc.png. If you photo is in jpg format, name the file as.pnganyway. - Indicate the different roles played and responsibilities held by each team member. You can reassign these
roles and responsibilities (as explained in Admin Project Scope) later in the project, if necessary.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
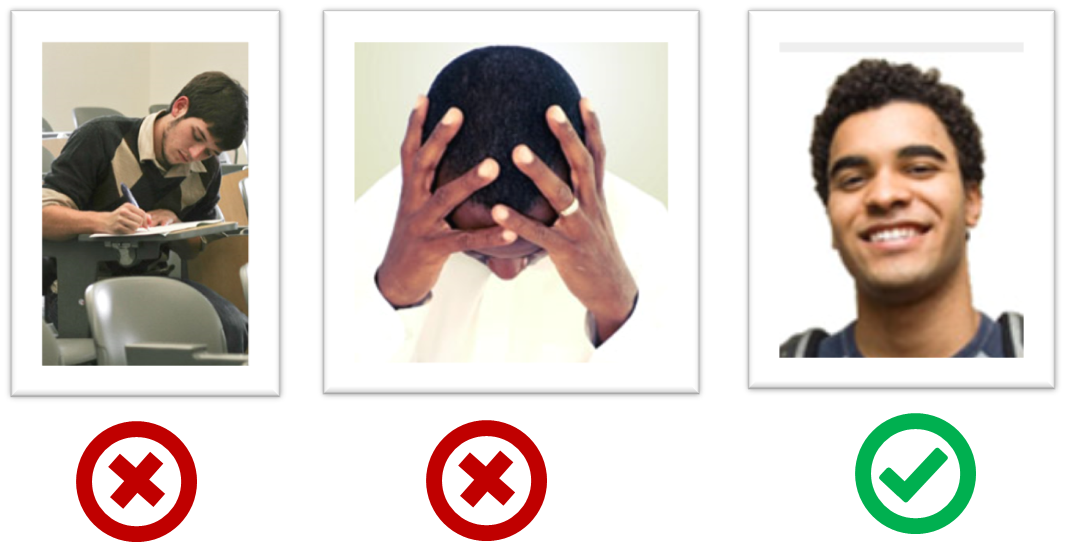
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
Roles indicate aspects you are in charge of and responsible for. E.g., if you are in charge of documentation, you are the person who should allocate which parts of the documentation is to be done by who, ensure the document is in right format, ensure consistency etc.
This is a non-exhaustive list; you may define additional roles.
- Team lead: Responsible for overall project coordination.
- Documentation (short for ‘in charge of documentation’): Responsible for the quality of various project documents.
- Testing: Ensures the testing of the project is done properly and on time.
- Code quality: Looks after code quality, ensures adherence to coding standards, etc.
- Deliverables and deadlines: Ensure project deliverables are done on time and in the right format.
- Integration: In charge of versioning of the code, maintaining the code repository, integrating various parts of the software to create a whole.
- Scheduling and tracking: In charge of defining, assigning, and tracking project tasks.
- [Tool ABC] expert: e.g. Intellij expert, Git expert, etc. Helps other team member with matters related to the specific tool.
- In charge of[Component XYZ]: e.g. In charge of
Model,UI,Storage, etc. If you are in charge of a component, you are expected to know that component well, and review changes done to that component in v1.3-v1.4.
Please make sure each of the important roles are assigned to one person in the team. It is OK to have a 'backup' for each role, but for each aspect there should be one person who is unequivocally the person responsible for it.
-
Contact Us Page: Update to match your product.
-
README.adoc page: Update it to match your project.
-
Add a UI mockup of your intended final product.
Note that the image of the UI should bedocs/images/Ui.pngso that it can be downloaded by our scripts. Limit the file to contain one screenshot/mockup only and ensure the new image is roughly the sameheight x widthproportions as the original one. Reason: when we compile these images from all teams into one page (example), yours should not look out of place. -
The original
README.adocfile (which doubles as the landing page of your project website) is written to read like the introduction to an SE learning/teaching resource. You should restructure this page to look like the home page of a real product (not a school project) targeting real users e.g. remove references to addressbook-level3, Learning Outcomes etc. mention target users, add a marketing blurb etc. On a related note, also removeLearning Outcomeslink and related pages. -
Update the link of the Travis build status badge (
) so that it reflects the build status of your team repo.
For the other badges,- either set up the respective tool for your project (AB-4 Developer Guide has instructions on how to set up AppVeyor and Coveralls) and update the badges accordingly,
- or remove the badge.
-
Acknowledge the original source of the code i.e. AddressBook-Level4 project created by SE-EDU initiative at
https://github.com/se-edu/
-
-
User Guide: Start moving the content from your User Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the User Guide page in your repository. If a feature is not implemented, mark it as 'Coming in v2.0' (example).
-
Developer Guide: Similar to the User Guide, start moving the content from your Developer Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the Developer Guide page in your team repository.
Product:
-
Each member can attempt to do a
local-impact change to the code base.Objective: To familiarize yourself with at least one
components of the product.Description: Divide the components among yourselves. Each member can do some small enhancements to their component(s) to learn the code of that component. Some suggested enhancements are given in the AddressBook-Level4 developer guide.
Submission: Create PRs from your own fork to your team repo. Get it merged by following your team's workflow.
5A. Process:
Evaluates: How well you did in project management related aspects of the project, as an individual and as a team
Based on: tutor/bot observations of project milestones and GitHub data
Milestones need to be reached the midnight before of the tutorial for it to be counted as achieved. To get a good grade for this aspect, achieve at least 60% of the recommended milestone progress.
Other criteria:
- Good use of GitHub milestones
- Good use of GitHub release mechanism
- Good version control, based on the repo
- Reasonable attempt to use the forking workflow
- Good task definition, assignment and tracking, based on the issue tracker
- Good use of buffers (opposite: everything at the last minute)
- Project done iteratively and incrementally (opposite: doing most of the work in one big burst)
5B. Team-tasks:
Evaluates: How much you contributed to team-tasks
Based on: peer evaluations, tutor observations
To earn full marks, you should have done a fair share of the team tasks. You can earn bonus marks by doing more than your fair share.
Relevant: [
Here is a non-exhaustive list of team-tasks:
- Necessary general code enhancements e.g.,
- Work related to renaming the product
- Work related to changing the product icon
- Morphing the product into a different product
- Setting up the GitHub, Travis, AppVeyor, etc.
- Maintaining the issue tracker
- Release management
- Updating user/developer docs that are not specific to a feature e.g. documenting the target user profile
- Incorporating more useful tools/libraries/frameworks into the product or the project workflow (e.g. automate more aspects of the project workflow using a GitHub plugin)
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
v1.1 Project Management
- Fix any errors in org/repo set up (e.g. wrong repo name).
- Wrap up the milestone using a git tag
v1.1as explained below:- When the milestone deadline is near (e.g., 0.5 days before the deadline), if you think some of the ongoing work intended for the current milestone may not finish in time, reassign them to a future milestone.
- After all changes that can be merged before the milestone deadline has been merged, use
git tagfeature to tag the current version with the milestone and push the tag to the team repo.
v1.1 Documentation
- Update User Guide, README, and About Us pages as described earlier in
mid-v1.1 progress guide .
Set up project repo, start moving UG and DG to the repo, attempt to do local-impact changes to the code base.
Project Management:
Set up the team org and the team repo as explained below:
Relevant: [
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Relevant: [
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
When updating code in the repo, follow the workflow explained below:
Relevant: [
Workflow
Before you do any coding for the project,
- Ensure you have
set the Git username correctly (as explained in Appendix E) in all Computers you use for coding. - Read
our reuse policy (in Admin: Appendix B) , in particular, how to give credit when you reuse code from the Internet or classmates:
Setting Git Username to Match GitHub Username
We use various tools to analyze your code. For us to be able to identify your commits, you should use the GitHub username as your Git username as well. If there is a mismatch, or if you use multiple user names for Git, our tools might miss some of your work and as a result you might not get credit for some of your work.
In each Computer you use for coding, after installing Git, you should set the Git username as follows.
- Open a command window that can run Git commands (e.g., Git bash window)
- Run the command
git config --global user.name YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME
e.g.,git config --global user.name JohnDoe
More info about setting Git username is here.
Policy on reuse
Reuse is encouraged. However, note that reuse has its own costs (such as the learning curve, additional complexity, usage restrictions, and unknown bugs). Furthermore, you will not be given credit for work done by others. Rather, you will be given credit for using work done by others.
- You are allowed to reuse work from your classmates, subject to following conditions:
- The work has been published by us or the authors.
- You clearly give credit to the original author(s).
- You are allowed to reuse work from external sources, subject to following conditions:
- The work comes from a source of 'good standing' (such as an established open source project). This means you cannot reuse code written by an outside 'friend'.
- You clearly give credit to the original author. Acknowledge use of third party resources clearly e.g. in the welcome message, splash screen (if any) or under the 'about' menu. If you are open about reuse, you are less likely to get into trouble if you unintentionally reused something copyrighted.
- You do not violate the license under which the work has been released. Please do not use 3rd-party images/audio in your software unless they have been specifically released to be used freely. Just because you found it in the Internet does not mean it is free for reuse.
- Always get permission from us before you reuse third-party libraries. Please post your 'request to use 3rd party library' in our forum. That way, the whole class get to see what libraries are being used by others.
Giving credit for reused work
Given below are how to give credit for things you reuse from elsewhere. These requirements are specific to this module i.e., not applicable outside the module (outside the module you should follow the rules specified by your employer and the license of the reused work)
If you used a third party library:
- Mention in the
README.adoc(under the Acknowledgements section) - mention in the
Project Portfolio Page if the library has a significant relevance to the features you implemented
If you reused code snippets found on the Internet e.g. from StackOverflow answers or
referred code in another software or
referred project code by current/past student:
- If you read the code to understand the approach and implemented it yourself, mention it as a comment
Example://Solution below adapted from https://stackoverflow.com/a/16252290 {Your implmentation of the reused solution here ...} - If you copy-pasted a non-trivial code block (possibly with minor modifications renaming, layout changes, changes to comments, etc.), also mark the code block as reused code (using
@@authortags
Format://@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused //{Info about the source...} {Reused code (possibly with minor modifications) here ...} //@@authorpersons = getList() //@@author johndoe-reused //Reused from https://stackoverflow.com/a/34646172 with minor modifications Collections.sort(persons, new Comparator<CustomData>() { @Override public int compare(CustomData lhs, CustomData rhs) { return lhs.customInt > rhs.customInt ? -1 : (lhs.customInt < rhs.customInt) ? 1 : 0; } }); //@@author return persons;
Adding @@author tags indicate authorship
-
Mark your code with a
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}. Note the double@.
The//@@authortag should indicates the beginning of the code you wrote. The code up to the next//@@authortag or the end of the file (whichever comes first) will be considered as was written by that author. Here is a sample code file://@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author sarahkhoo method 3 ... //@@author johndoe method 4 ... -
If you don't know who wrote the code segment below yours, you may put an empty
//@@author(i.e. no GitHub username) to indicate the end of the code segment you wrote. The author of code below yours can add the GitHub username to the empty tag later. Here is a sample code with an emptyauthortag:method 0 ... //@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author method 3 ... method 4 ... -
The author tag syntax varies based on file type e.g. for java, css, fxml. Use the corresponding comment syntax for non-Java files.
Here is an example code from an xml/fxml file.<!-- @@author sereneWong --> <textbox> <label>...</label> <input>...</input> </textbox> ... -
Do not put the
//@@authorinside java header comments.
👎/** * Returns true if ... * @@author johndoe */👍
//@@author johndoe /** * Returns true if ... */
What to and what not to annotate
-
Annotate both functional and test code There is no need to annotate documentation files.
-
Annotate only significant size code blocks that can be reviewed on its own e.g., a class, a sequence of methods, a method.
Claiming credit for code blocks smaller than a method is discouraged but allowed. If you do, do it sparingly and only claim meaningful blocks of code such as a block of statements, a loop, or an if-else statement.- If an enhancement required you to do tiny changes in many places, there is no need to annotate all those tiny changes; you can describe those changes in the Project Portfolio page instead.
- If a code block was touched by more than one person, either let the person who wrote most of it (e.g. more than 80%) take credit for the entire block, or leave it as 'unclaimed' (i.e., no author tags).
- Related to the above point, if you claim a code block as your own, more than 80% of the code in that block should have been written by yourself. For example, no more than 20% of it can be code you reused from somewhere.
- 💡 GitHub has a blame feature and a history feature that can help you determine who wrote a piece of code.
-
Do not try to boost the quantity of your contribution using unethical means such as duplicating the same code in multiple places. In particular, do not copy-paste test cases to create redundant tests. Even repetitive code blocks within test methods should be extracted out as utility methods to reduce code duplication. Individual members are responsible for making sure code attributed to them are correct. If you notice a team member claiming credit for code that he/she did not write or use other questionable tactics, you can email us (after the final submission) to let us know.
-
If you wrote a significant amount of code that was not used in the final product,
- Create a folder called
{project root}/unused - Move unused files (or copies of files containing unused code) to that folder
- use
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-unusedto mark unused code in those files (note the suffixunused) e.g.
//@@author johndoe-unused method 1 ... method 2 ...Please put a comment in the code to explain why it was not used.
- Create a folder called
-
If you reused code from elsewhere, mark such code as
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused(note the suffixreused) e.g.//@@author johndoe-reused method 1 ... method 2 ... -
You can use empty
@@authortags to mark code as not yours when RepoSense attribute the to you incorrectly.-
Code generated by the IDE/framework, should not be annotated as your own.
-
Code you modified in minor ways e.g. adding a parameter. These should not be claimed as yours but you can mention these additional contributions in the Project Portfolio page if you want to claim credit for them.
-
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Features implemented: A summary of the features you implemented. If you implemented multiple features, you are recommended to indicate which one is the biggest feature.
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP
-
-
Page limit:
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 (soft limit) Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 (soft limit) Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 (soft limit) Total 5-10 (strict) - The page limits given above are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
- Reason for page limit: These submissions are peer-graded (in the PE) which needs to be done in a limited time span.
If you have more content than the limit given above, you can give a representative samples of UG and DG that showcase your documentation skills. Those samples should be understandable on their own. For the parts left-out, you can give an abbreviated version and refer the reader to the full UG/DG for more details.
It's similar to giving extra details as appendices; the reader will look at the UG/DG if the PPP is not enough to make a judgment. For example, when judging documentation quality, if the part in the PPP is not well-written, there is no point reading the rest in the main UG/DG. That's why you need to put the most representative part of your writings in the PPP and still give an abbreviated version of the rest in the PPP itself. Even when judging the quantity of work, the reader should be able to get a good sense of the quantity by combining what is quoted in the PPP and your abbreviated description of the missing part. There is no guarantee that the evaluator will read the full document.
Follow the
- Get team members to review PRs. A workflow without PR reviews is a risky workflow.
- Do not merge PRs failing
CI . After setting up Travis, the CI status of a PR is reported at the bottom of the PR page. The screenshot below shows the status of a PR that is passing all CI checks.

If there is a failure, you can click on theDetailslink in corresponding line to find out more about the failure. Once you figure out the cause of the failure, push the a fix to the PR. - After setting up Netlify, you can use Netlify PR Preview to preview changes to documentation files, if the PR contains updates to documentation. To see the preview, click on the
Detailslink in front of the Netlify status reported (refer screenshot above).
After completing v1.1, you can adjust process rigor to suit your team's pace, as explained below.
-
Reduce automated tests have benefits, but they can be a pain to write/maintain; GUI tests are especially hard to maintain because their behavior can sometimes depend on things such as the OS, resolution etc.
It is OK to get rid of some of the troublesome tests and rely more on manual testing instead. The less automated tests you have, the higher the risk of regressions; but it may be an acceptable trade-off under the circumstances if tests are slowing you down too much.
There is no direct penalty for removing GUI tests. Also noteour expectation on test code . -
Reduce automated checks: You can also reduce the rigor of checkstyle checks to expedite PR processing.
-
Switch to a lighter workflow: While forking workflow is the safest, it is also rather heavy. You an switch to a simpler workflow if the forking workflow is slowing you down. Refer the textbook to find more about alternative workflows: branching workflow, centralized workflow. However, we still recommend that you use PR reviews, at least for PRs affecting others' features.
You can also increase the rigor/safety of your workflow in the following ways:
- Use GitHub's Protected Branches feature to protect your
masterbranch against rogue PRs.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
Project Management → Revision Control →

In the forking workflow, the 'official' version of the software is kept in a remote repo designated as the 'main repo'. All team members fork the main repo create pull requests from their fork to the main repo.
To illustrate how the workflow goes, let’s assume Jean wants to fix a bug in the code. Here are the steps:
- Jean creates a separate branch in her local repo and fixes the bug in that branch.
- Jean pushes the branch to her fork.
- Jean creates a pull request from that branch in her fork to the main repo.
- Other members review Jean’s pull request.
- If reviewers suggested any changes, Jean updates the PR accordingly.
- When reviewers are satisfied with the PR, one of the members (usually the team lead or a designated 'maintainer' of the main repo) merges the PR, which brings Jean’s code to the main repo.
- Other members, realizing there is new code in the upstream repo, sync their forks with the new upstream repo (i.e. the main repo). This is done by pulling the new code to their own local repo and pushing the updated code to their own fork.
- A detailed explanation of the Forking Workflow - From Atlassian
Documentation:
Recommended procedure for updating docs:
- Divide among yourselves who will update which parts of the document(s).
- Update the team repo by following the workflow mentioned above.
Update the following pages in your project repo:
- About Us page:
This page is used for module admin purposes. Please follow the format closely or else our scripts will not be able to give credit for your work.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
here . - Including the name/photo of the supervisor/lecturer is optional.
- The photo of a team member should be
doc/images/githbub_username_in_lower_case.pnge.g.docs/images/damithc.png. If you photo is in jpg format, name the file as.pnganyway. - Indicate the different roles played and responsibilities held by each team member. You can reassign these
roles and responsibilities (as explained in Admin Project Scope) later in the project, if necessary.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
Roles indicate aspects you are in charge of and responsible for. E.g., if you are in charge of documentation, you are the person who should allocate which parts of the documentation is to be done by who, ensure the document is in right format, ensure consistency etc.
This is a non-exhaustive list; you may define additional roles.
- Team lead: Responsible for overall project coordination.
- Documentation (short for ‘in charge of documentation’): Responsible for the quality of various project documents.
- Testing: Ensures the testing of the project is done properly and on time.
- Code quality: Looks after code quality, ensures adherence to coding standards, etc.
- Deliverables and deadlines: Ensure project deliverables are done on time and in the right format.
- Integration: In charge of versioning of the code, maintaining the code repository, integrating various parts of the software to create a whole.
- Scheduling and tracking: In charge of defining, assigning, and tracking project tasks.
- [Tool ABC] expert: e.g. Intellij expert, Git expert, etc. Helps other team member with matters related to the specific tool.
- In charge of[Component XYZ]: e.g. In charge of
Model,UI,Storage, etc. If you are in charge of a component, you are expected to know that component well, and review changes done to that component in v1.3-v1.4.
Please make sure each of the important roles are assigned to one person in the team. It is OK to have a 'backup' for each role, but for each aspect there should be one person who is unequivocally the person responsible for it.
-
Contact Us Page: Update to match your product.
-
README.adoc page: Update it to match your project.
-
Add a UI mockup of your intended final product.
Note that the image of the UI should bedocs/images/Ui.pngso that it can be downloaded by our scripts. Limit the file to contain one screenshot/mockup only and ensure the new image is roughly the sameheight x widthproportions as the original one. Reason: when we compile these images from all teams into one page (example), yours should not look out of place. -
The original
README.adocfile (which doubles as the landing page of your project website) is written to read like the introduction to an SE learning/teaching resource. You should restructure this page to look like the home page of a real product (not a school project) targeting real users e.g. remove references to addressbook-level3, Learning Outcomes etc. mention target users, add a marketing blurb etc. On a related note, also removeLearning Outcomeslink and related pages. -
Update the link of the Travis build status badge (
) so that it reflects the build status of your team repo.
For the other badges,- either set up the respective tool for your project (AB-4 Developer Guide has instructions on how to set up AppVeyor and Coveralls) and update the badges accordingly,
- or remove the badge.
-
Acknowledge the original source of the code i.e. AddressBook-Level4 project created by SE-EDU initiative at
https://github.com/se-edu/
-
-
User Guide: Start moving the content from your User Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the User Guide page in your repository. If a feature is not implemented, mark it as 'Coming in v2.0' (example).
-
Developer Guide: Similar to the User Guide, start moving the content from your Developer Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the Developer Guide page in your team repository.
Product:
-
Each member can attempt to do a
local-impact change to the code base.Objective: To familiarize yourself with at least one
components of the product.Description: Divide the components among yourselves. Each member can do some small enhancements to their component(s) to learn the code of that component. Some suggested enhancements are given in the AddressBook-Level4 developer guide.
Submission: Create PRs from your own fork to your team repo. Get it merged by following your team's workflow.
-
Update Developer Guide page with user stories and use cases. Refer to
mid-v1.0. Submission: Merge your changes to the master branch of your repo. Create a PR with your changes.
Decide on requirements (user stories, use cases, non-functional requirements).
💡 Given below are some guidance on the recommended progress at this point of the project (i.e., at week 4, which is the midway point of the milestone v1.0)
This is a good time to analyze requirements with a view to conceptualizing the next version of the product (i.e. v2.0).
-
Step 1 : Brainstorm user stories

Get together with your team members and
brainstorm foruser stories for the v2.0 of the product. Note that in the module project you will deliver only up to v1.4 but here you should consider up to v2.0 (i.e. beyond the module).-
It is ok to have more user stories than you can deliver in the project. Aim to create at least 30 user stories. Include all 'obvious' ones you can think of but also look for 'non obvious' ones that you think are likely to be missed by other teams.
-
Refer
[Textbook Specifying Requirements → UserStories → Usage → (section) Tips] for tips on how to use user stories in this task. -
You can write each user story in a piece of paper (e.g. yellow sticky note, index card, or just pieces of paper about the size of a playing card). Alternatively you can use an online tool (some examples given in
[Textbook Specifying Requirements → UserStories → Usage → (panel) Tool Examples ] ). -
Note that you should not 'evaluate' the value of user stories while doing the above. Reason: an important aspect of brainstorming is not judging the ideas generated.
-
Requirements → Gathering Requirements →
Brainstorming: A group activity designed to generate a large number of diverse and creative ideas for the solution of a problem.
In a brainstorming session there are no "bad" ideas. The aim is to generate ideas; not to validate them. Brainstorming encourages you to "think outside the box" and put "crazy" ideas on the table without fear of rejection.
What is the key characteristic about brainstorming?
(b)
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → User Stories →
User story: User stories are short, simple descriptions of a feature told from the perspective of the person who desires the new capability, usually a user or customer of the system. [Mike Cohn]
A common format for writing user stories is:
User story format: As a {user type/role} I can {function} so that {benefit}
Examples (from a Learning Management System):
- As a student, I can download files uploaded by lecturers, so that I can get my own copy of the files
- As a lecturer, I can create discussion forums, so that students can discuss things online
- As a tutor, I can print attendance sheets, so that I can take attendance during the class
We can write user stories on index cards or sticky notes, and arrange on walls or tables, to facilitate planning and discussion. Alternatively, we can use a software (e.g., GitHub Project Boards, Trello, Google Docs, ...) to manage user stories digitally.


[credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jakuza/with/2726048607/]
[credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:User_Story_Map_in_Action.png]
- a. They are based on stories users tell about similar systems
- b. They are written from the user/customer perspective
- c. They are always written in some physical medium such as index cards or sticky notes
- a. Reason: Despite the name, user stories are not related to 'stories' about the software.
- b.
- c. Reason: It is possible to use software to record user stories. When the team members are not co-located this may be the only option.
Critique the following user story taken from a software project to build an e-commerce website.
As a developer, I want to use Python to implement the software, so that we can resue existing Python modules.
Refer to the definition of a user story.
User story: User stories are short, simple descriptions of a feature told from the perspective of the person who desires the new capability, usually a user or customer of the system. [Mike Cohn]
This user story is not written from the perspective of the user/customer.
Bill wants you to build a Human Resource Management (HRM) system. He mentions that the system will help employees to view their own
Remember to follow the correct format when writing user stories.
User story format: As a {user type/role} I can {function} so that {benefit}
As an employee, I can view my leave balance, so that I can know how many leave days I have left.
Note: the {benefit} part may vary as it is not specifically mentioned in the question.
You can create issues for each of the user stories and use a GitHub Project Board to sort them into categories.
Example Project Board:
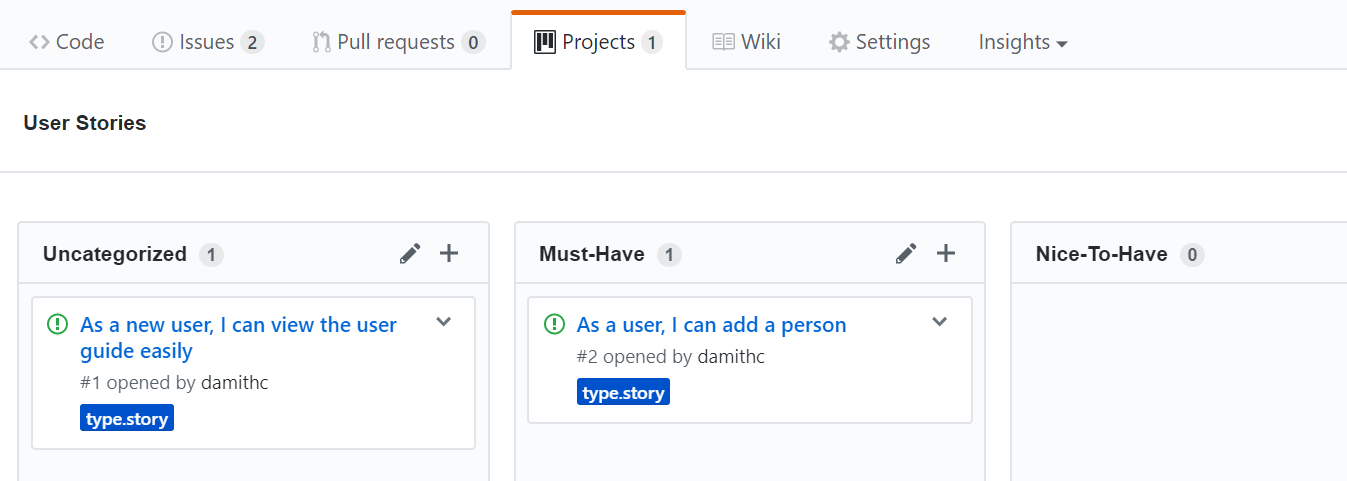
Example Issue to represent a user story:
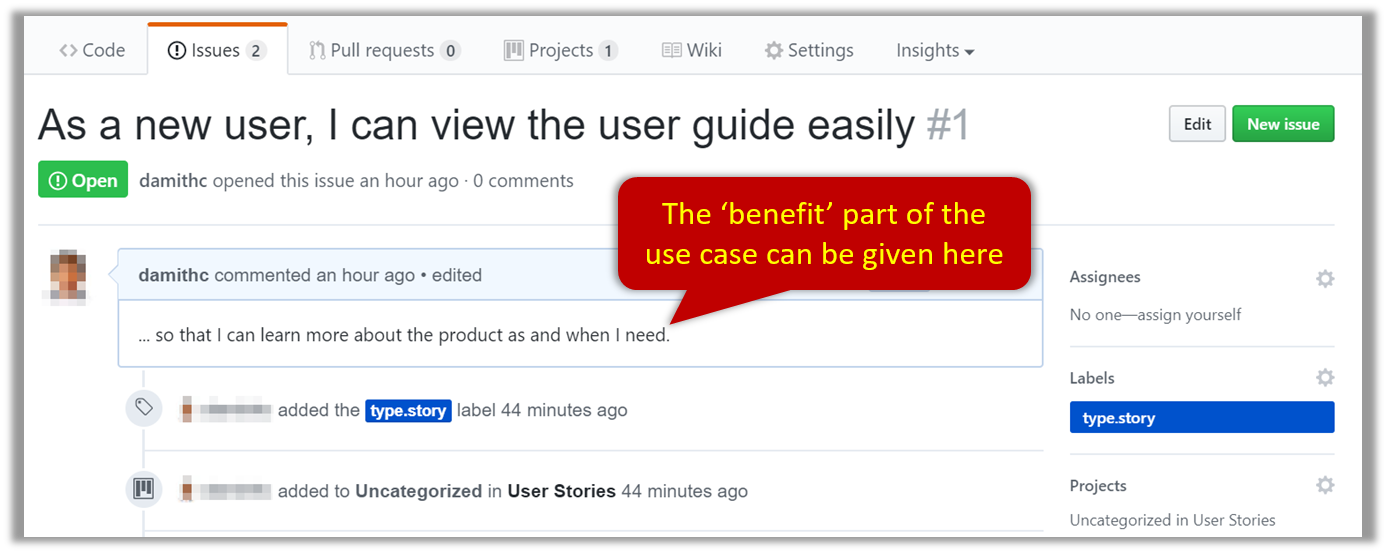
A video on GitHub Project Boards:
Example Google Sheet for recording user stories:
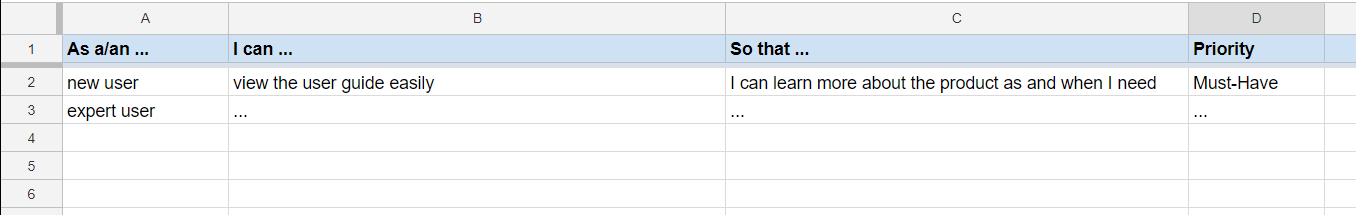
Example Trello Board for recording user stories:
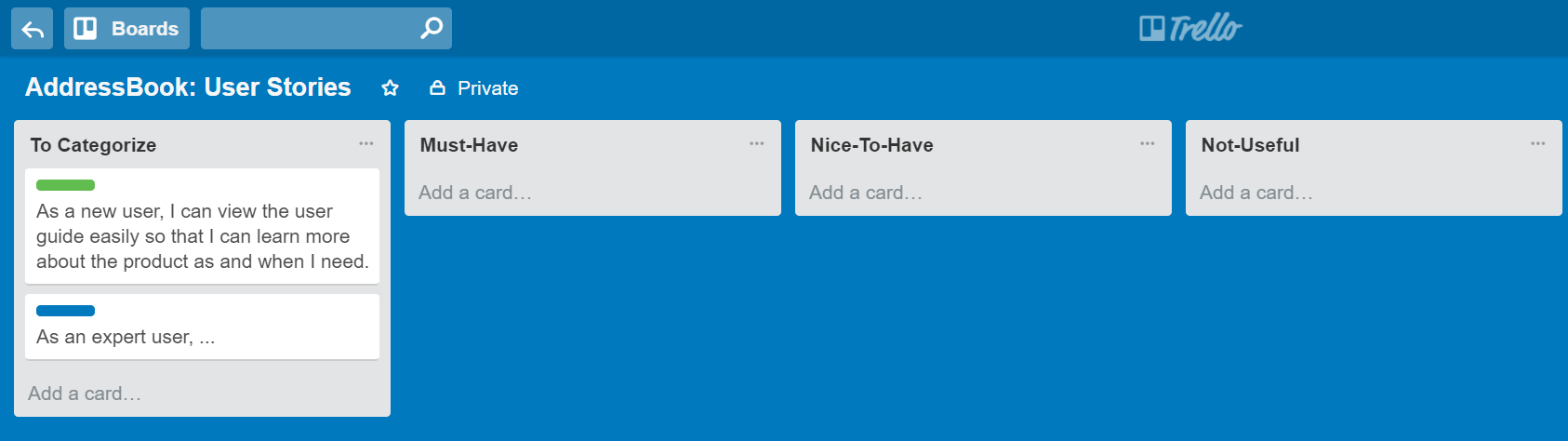
Given their lightweight nature, user stories are quite handy for recording requirements during early stages of requirements gathering.
💡 Here are some tips for using user stories for early stages of requirement gathering:
- Define the target user:
Decide your target user's profile (e.g. a student, office worker, programmer, sales person) and work patterns (e.g. Does he work in groups or alone? Does he share his computer with others?). A clear understanding of the target user will help when deciding the importance of a user story. You can even give this user a name. e.g. Target user Jean is a university student studying in a non-IT field. She interacts with a lot of people due to her involvement in university clubs/societies. ... - Define the problem scope: Decide that exact problem you are going to solve for the target user. e.g. Help Jean keep track of all her school contacts
- Don't be too hasty to discard 'unusual' user stories:
Those might make your product unique and stand out from the rest, at least for the target users. - Don't go into too much details:
For example, consider this user story:As a user, I want to see a list of tasks that needs my attention most at the present time, so that I pay attention to them first.
When discussing this user story, don't worry about what tasks should be considered needs my attention most at the present time. Those details can be worked out later. - Don't be biased by preconceived product ideas:
When you are at the stage of identifying user needs, clear your mind of ideas you have about what your end product will look like. - Don't discuss implementation details or whether you are actually going to implement it:
When gathering requirements, your decision is whether the user's need is important enough for you to want to fulfil it. Implementation details can be discussed later. If a user story turns out to be too difficult to implement later, you can always omit it from the implementation plan.
💡 Recommended: You can use GitHub issue tracker to manage user stories, but for that you need to set up your team's GitHub organization, project fork, and issue tracker first. Instructions for doing those steps are in the panel below.
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
Issue tracker setup
We recommend you configure the issue tracker of the main repo as follows:
- Delete existing labels and add the following labels.
💡 Issue type labels are useful from the beginning of the project. The other labels are needed only when you start implementing the features.
Issue type labels:
type.Epic: A big feature which can be broken down into smaller stories e.g. searchtype.Story: A user storytype.Enhancement: An enhancement to an existing storytype.Task: Something that needs to be done, but not a story, bug, or an epic. e.g. Move testing code into a new folder)type.Bug: A bug
Status labels:
status.Ongoing: The issue is currently being worked on. note: remove this label before closing an issue.
Priority labels:
priority.High: Must dopriority.Medium: Nice to havepriority.Low: Unlikely to do
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Create following milestones :
v1.0,v1.1,v1.2,v1.3,v1.4, -
You may configure other project settings as you wish. e.g. more labels, more milestones
Project Schedule Tracking
In general, use the issue tracker (Milestones, Issues, PRs, Tags, Releases, and Labels) for assigning, scheduling, and tracking all noteworthy project tasks, including user stories. Update the issue tracker regularly to reflect the current status of the project. You can also use GitHub's Projects feature to manage the project, but keep it linked to the issue tracker as much as you can.
Using Issues:
During the initial stages (latest by the start of v1.2):
-
Record each of the user stories you plan to deliver as an issue in the issue tracker. e.g.
Title: As a user I can add a deadline
Description: ... so that I can keep track of my deadlines -
Assign the
type.*andpriority.*labels to those issues. -
Formalize the project plan by assigning relevant issues to the corresponding milestone.
From milestone v1.2:
-
Define project tasks as issues. When you start implementing a user story (or a feature), break it down to smaller tasks if necessary. Define reasonable sized, standalone tasks. Create issues for each of those tasks so that they can be tracked.e.g.
-
A typical task should be able to done by one person, in a few hours.
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
Write the Developer Guide - Good:
Update class diagram in the Developer Guide for v1.4
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
-
There is no need to break things into VERY small tasks. Keep them as big as possible, but they should be no bigger than what you are going to assign a single person to do within a week. eg.,
- Bad:
Implementing parser(reason: too big). - Good:
Implementing parser support for adding of floating tasks
- Bad:
-
Do not track things taken for granted. e.g.,
push code to reposhould not be a task to track. In the example given under the previous point, it is taken for granted that the owner will also (a) test the code and (b) push to the repo when it is ready. Those two need not be tracked as separate tasks. -
Write a descriptive title for the issue. e.g.
Add support for the 'undo' command to the parser- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
prioritycan be omitted if you think they don't help you.
- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
-
-
Assign tasks (i.e., issues) to the corresponding team members using the
assigneesfield. Normally, there should be some ongoing tasks and some pending tasks against each team member at any point. -
Optionally, you can use
status.ongoinglabel to indicate issues currently ongoing.
Using Milestones:
We recommend you do proper milestone management starting from v1.2. Given below are the conditions to satisfy for a milestone to be considered properly managed:
Planning a Milestone:
-
Issues assigned to the milestone, team members assigned to issues: Used GitHub milestones to indicate which issues are to be handled for which milestone by assigning issues to suitable milestones. Also make sure those issues are assigned to team members. Note that you can change the milestone plan along the way as necessary.
-
Deadline set for the milestones (in the GitHub milestone). Your internal milestones can be set earlier than the deadlines we have set, to give you a buffer.
Wrapping up a Milestone:
-
A working product tagged with the correct tag (e.g.
v1.2) and is pushed to the main repo
or a product release done on GitHub. A product release is optional for v1.2 but required from from v1.3. Click here to see an example release. -
All tests passing on Travis for the version tagged/released.
-
Milestone updated to match the product i.e. all issues completed and PRs merged for the milestone should be assigned to the milestone. Incomplete issues/PRs should be moved to a future milestone.
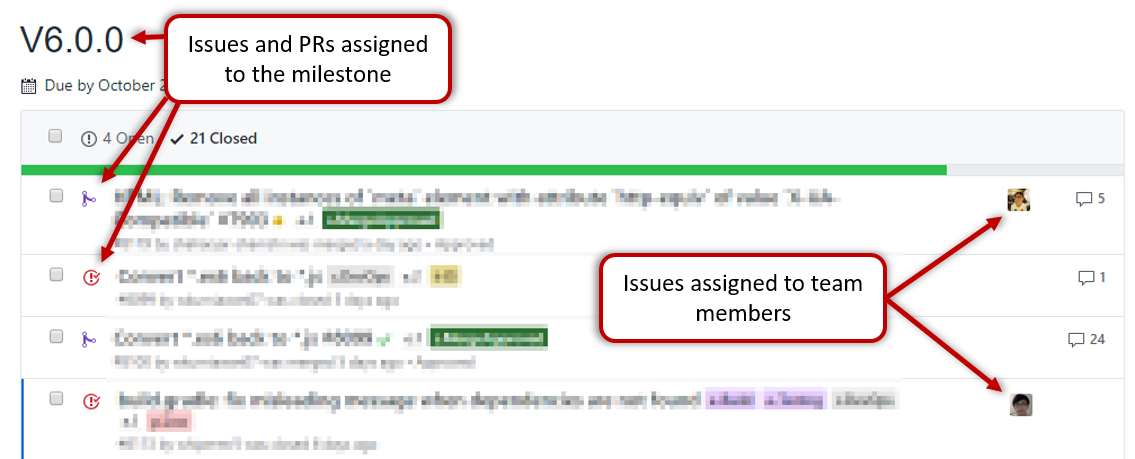
-
Milestone closed.
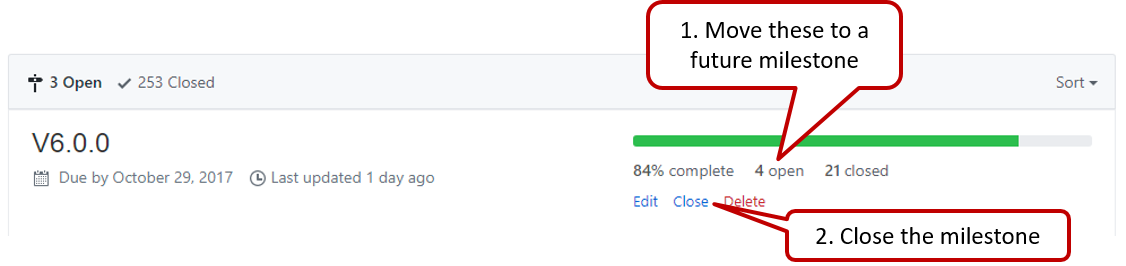
-
If necessary, future milestones are revised based on what you experienced in the current milestone e.g. if you could not finish all issues assigned to the current milestone, it is a sign that you overestimated how much you can do in a week, which means you might want to reduce the issues assigned to future milestones to match that observation.
As a user I can add a task by specifying a task description only, so that I can record tasks that need to be done ‘some day’.
As a user I can find upcoming tasks, so that I can decide what needs to be done soon.
As a user I can delete a task, so that I can get rid of tasks that I no longer care to track.
As a new user I can view more information about a particular command, so that I can learn how to use various commands.
As an advanced user I can use shorter versions of a command, so that type a command faster.
-
Step 2: Prioritize the user stories

Suggested workflow:
-
Take one user story at a time and get team member opinions about it.
-
Based on the team consensus, put the story (i.e. the piece of paper) onto one of these three piles:
Must-Have: The product will be practically useless to the target user without this feature.Nice-To-Have: The target user can benefit from this user story significantly but you are not certain if you'll have time to implement it.Not-Useful: No significant benefit to the target user, or does not fit into the product vision.
-
If using physical paper to record user stories: After all stories have been put in the above three piles, you can make a record of which stories are in the three piles.
-
-
Step 3: Document requirements of the product
Based on your user story categorization in the step above, given module requirements/constraints for the project, and the current state of the product, select which user stories you are likely to include in v2.0.
Document the following items using a convenient format (e.g., a GoogleDoc). Do not spend time on formatting the content nicely; reason: these will be ported to the actual Developer Guide in your project repo later.
💡 Some examples of these can be found in the AB4 Developer Guide.- Target user profile, value proposition, and
user stories : Update the target user profile and value proposition to match the project direction you have selected. Give a list of the user stories (and update/delete existing ones, if applicable), including priorities. This can include user stories considered but will not be included in the final product. -
Use cases : Give use cases (textual form) for a few representative user stories that need multiple steps to complete. e.g. Adding a tag to a person (assume the user needs to find the person first) -
Non-functional requirements :
Note: Many of the project constraints mentioned above are NFRs. You can add more. e.g. performance requirements, usability requirements, scalability requirements, etc. -
Glossary : Define terms that are worth defining. - [Optional]
Product survey : Explore a few similar/related products and describe your findings i.e. Pros, cons, (from the target user's point of view).
- Target user profile, value proposition, and
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → Use Cases →
Use Case: A description of a set of sequences of actions, including variants, that a system performs to yield an observable result of value to an
Actor: An actor (in a use case) is a role played by a user. An actor can be a human or another system. Actors are not part of the system; they reside outside the system.
A use case describes an interaction between the user and the system for a specific functionality of the system.
- System:
ATM - Actor: Customer
- Use Case: Check account balance
- User inserts an ATM card
- ATM prompts for PIN
- User enters PIN
- ATM prompts for withdrawal amount
- User enters the amount
- ATM ejects the ATM card and issues cash
- User collects the card and the cash.
- System: A Learning Management System (LMS)
- Actor: Student
- Use Case: Upload file
- Student requests to upload file
- LMS requests for the file location
- Student specifies the file location
- LMS uploads the file
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a graphical notation to describe various aspects of a software system. UML is the brainchild of three software modeling specialists James Rumbaugh, Grady Booch and Ivar Jacobson (also known as the Three Amigos). Each of them has developed their own notation for modeling software systems before joining force to create a unified modeling language (hence, the term ‘Unified’ in UML). UML is currently the de facto modeling notation used in the software industry.
Use cases capture the functional requirements of a system.
Requirements → Requirements →
There are two kinds of requirements:
- Functional requirements specify what the system should do.
- Non-functional requirements specify the constraints under which system is developed and operated.
Some examples of non-functional requirement categories:
- Data requirements e.g. size,
volatility ,persistency etc., - Environment requirements e.g. technical environment in which system would operate or need to be compatible with.
- Accessibility, Capacity, Compliance with regulations, Documentation, Disaster recovery, Efficiency, Extensibility, Fault tolerance, Interoperability, Maintainability, Privacy, Portability, Quality, Reliability, Response time, Robustness, Scalability, Security, Stability, Testability, and more ...
- Business/domain rules: e.g. the size of the minefield cannot be smaller than five.
- Constraints: e.g. the system should be backward compatible with data produced by earlier versions of the system; system testers are available only during the last month of the project; the total project cost should not exceed $1.5 million.
- Technical requirements: e.g. the system should work on both 32-bit and 64-bit environments.
- Performance requirements: e.g. the system should respond within two seconds.
- Quality requirements: e.g. the system should be usable by a novice who has never carried out an online purchase.
- Process requirements: e.g. the project is expected to adhere to a schedule that delivers a feature set every one month.
- Notes about project scope: e.g. the product is not required to handle the printing of reports.
- Any other noteworthy points: e.g. the game should not use images deemed offensive to those injured in real mine clearing activities.
We may have to spend an extra effort in digging NFRs out as early as possible because,
- NFRs are easier to miss e.g., stakeholders tend to think of functional requirements first
- sometimes NFRs are critical to the success of the software. E.g. A web application that is too slow or that has low security is unlikely to succeed even if it has all the right functionality.
Given below are some requirements of TEAMMATES (an online peer evaluation system for education). Which one of these are non-functional requirements?
- a. The response to any use action should become visible within 5 seconds.
- b. The application admin should be able to view a log of user activities.
- c. The source code should be open source.
- d. A course should be able to have up to 2000 students.
- e. As a student user, I can view details of my team members so that I can know who they are.
- f. The user interface should be intuitive enough for users who are not IT-savvy.
- g. The product is offered as a free online service.
(a)(c)(d)(f)(g)
Explanation: (b) are (e) are functions available for a specific user types. Therefore, they are functional requirements. (a), (c), (d), (f) and (g) are either constraints on functionality or constraints on how the project is done, both of which are considered non-functional requirements.
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → Glossary →
Glossary: A glossary serves to ensure that all stakeholders have a common understanding of the noteworthy terms, abbreviation, acronyms etc.
Here is a partial glossary from a variant of the Snakes and Ladders game:
- Conditional square: A square that specifies a specific face value which a player has to throw before his/her piece can leave the square.
- Normal square: a normal square does not have any conditions, snakes, or ladders in it.
Requirements → Gathering Requirements →
Studying existing products can unearth shortcomings of existing solutions that can be addressed by a new product. Product manuals and other forms of technical documentation of an existing system can be a good way to learn about how the existing solutions work.
When developing a game for a mobile device, a look at a similar PC game can give insight into the kind of features and interactions the mobile game can offer.
Tutors will provide feedback on this version of the UG and DG. This feedback should be used to improve your final submission.
v1.1 Product
- Each member should try to add some enhancements that are in line with the vision for v2.0. After adding some local-impact changes as recommended in
mid-v1.1 progress guide , attempt to do someglobal-impact enhancements , touching as many other components as possible. Refer to the AddressBook-Level4 Developer Guide has some guidance on how to implement a new feature end-to-end.
Suggested tutorial activity
- Discuss the architecture of your project with the other team and your tutor.
Questions to discuss during tutorial:
- Which architecture styles are used by AB-4?
- What is an API? How is it used in AB-4?
Explain the interactions depicted in this sequence diagram.

First, the createParser() method of an existing ParserFactory object is called. Then, ...
Draw a sequence diagram to represent this code snippet.
if (isFirstPage) {
new Quote().print();
}
The Quote class:
class Quote{
String q;
Quote(){
q = generate();
}
String generate(){
// ...
}
void print(){
System.out.println(q);
}
}
- Show
new Quote().print();as two method calls. - As the created Quote object is not assigned to a variable, it can be considered as 'deleted' soon after its
print()method is called.
- What’s the difference between buffers and padding/inflating estimates?
Update UG in the repo, attempt to do global-impact changes to the code base.
Milestone progress is graded. Be reminded that reaching individual and team milestones are considered for
Most aspects project progress are tracked using automated scripts. Please follow our instructions closely or else the script will not be able to detect your progress. We prefer not to spend admin resources processing requests for partial credit for work that did not follow the instructions precisely, unless the progress was not detected due to a bug in the script.
Milestone requirements are cumulative. The recommended progress for the mid-milestone is an implicit requirement for the actual milestone unless a milestone requirement overrides a mid-milestone requirement e.g., mid-milestone requires a document to be in a temp format while the actual milestone requires it to be in the proper format. Similarly, a requirement for milestone n is also an implicit requirement for milestone n+1 unless n+1 overrides the n requirement. This means if you miss some requirement at milestone n, you should try to achieve it before milestone n+1 or else it could be noted again as a 'missed requirement' at milestone n+1.
v1.1 Summary of Milestone
| Milestone | Minimum acceptable performance to consider as 'reached' |
|---|---|
| Team org/repo set up | as stated in |
| Some code enhancements done | created PRs to do local/global changes |
| Photo uploaded | a photo complying to |
| Project docs updated | updated docs are merged to the master branch |
| Milestone wrapped up | a commit in the master branch tagged as v1.1 |
Set up project repo, start moving UG and DG to the repo, attempt to do local-impact changes to the code base.
Project Management:
Set up the team org and the team repo as explained below:
Relevant: [
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Relevant: [
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
When updating code in the repo, follow the workflow explained below:
Relevant: [
Workflow
Before you do any coding for the project,
- Ensure you have
set the Git username correctly (as explained in Appendix E) in all Computers you use for coding. - Read
our reuse policy (in Admin: Appendix B) , in particular, how to give credit when you reuse code from the Internet or classmates:
Setting Git Username to Match GitHub Username
We use various tools to analyze your code. For us to be able to identify your commits, you should use the GitHub username as your Git username as well. If there is a mismatch, or if you use multiple user names for Git, our tools might miss some of your work and as a result you might not get credit for some of your work.
In each Computer you use for coding, after installing Git, you should set the Git username as follows.
- Open a command window that can run Git commands (e.g., Git bash window)
- Run the command
git config --global user.name YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME
e.g.,git config --global user.name JohnDoe
More info about setting Git username is here.
Policy on reuse
Reuse is encouraged. However, note that reuse has its own costs (such as the learning curve, additional complexity, usage restrictions, and unknown bugs). Furthermore, you will not be given credit for work done by others. Rather, you will be given credit for using work done by others.
- You are allowed to reuse work from your classmates, subject to following conditions:
- The work has been published by us or the authors.
- You clearly give credit to the original author(s).
- You are allowed to reuse work from external sources, subject to following conditions:
- The work comes from a source of 'good standing' (such as an established open source project). This means you cannot reuse code written by an outside 'friend'.
- You clearly give credit to the original author. Acknowledge use of third party resources clearly e.g. in the welcome message, splash screen (if any) or under the 'about' menu. If you are open about reuse, you are less likely to get into trouble if you unintentionally reused something copyrighted.
- You do not violate the license under which the work has been released. Please do not use 3rd-party images/audio in your software unless they have been specifically released to be used freely. Just because you found it in the Internet does not mean it is free for reuse.
- Always get permission from us before you reuse third-party libraries. Please post your 'request to use 3rd party library' in our forum. That way, the whole class get to see what libraries are being used by others.
Giving credit for reused work
Given below are how to give credit for things you reuse from elsewhere. These requirements are specific to this module i.e., not applicable outside the module (outside the module you should follow the rules specified by your employer and the license of the reused work)
If you used a third party library:
- Mention in the
README.adoc(under the Acknowledgements section) - mention in the
Project Portfolio Page if the library has a significant relevance to the features you implemented
If you reused code snippets found on the Internet e.g. from StackOverflow answers or
referred code in another software or
referred project code by current/past student:
- If you read the code to understand the approach and implemented it yourself, mention it as a comment
Example://Solution below adapted from https://stackoverflow.com/a/16252290 {Your implmentation of the reused solution here ...} - If you copy-pasted a non-trivial code block (possibly with minor modifications renaming, layout changes, changes to comments, etc.), also mark the code block as reused code (using
@@authortags
Format://@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused //{Info about the source...} {Reused code (possibly with minor modifications) here ...} //@@authorpersons = getList() //@@author johndoe-reused //Reused from https://stackoverflow.com/a/34646172 with minor modifications Collections.sort(persons, new Comparator<CustomData>() { @Override public int compare(CustomData lhs, CustomData rhs) { return lhs.customInt > rhs.customInt ? -1 : (lhs.customInt < rhs.customInt) ? 1 : 0; } }); //@@author return persons;
Adding @@author tags indicate authorship
-
Mark your code with a
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}. Note the double@.
The//@@authortag should indicates the beginning of the code you wrote. The code up to the next//@@authortag or the end of the file (whichever comes first) will be considered as was written by that author. Here is a sample code file://@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author sarahkhoo method 3 ... //@@author johndoe method 4 ... -
If you don't know who wrote the code segment below yours, you may put an empty
//@@author(i.e. no GitHub username) to indicate the end of the code segment you wrote. The author of code below yours can add the GitHub username to the empty tag later. Here is a sample code with an emptyauthortag:method 0 ... //@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author method 3 ... method 4 ... -
The author tag syntax varies based on file type e.g. for java, css, fxml. Use the corresponding comment syntax for non-Java files.
Here is an example code from an xml/fxml file.<!-- @@author sereneWong --> <textbox> <label>...</label> <input>...</input> </textbox> ... -
Do not put the
//@@authorinside java header comments.
👎/** * Returns true if ... * @@author johndoe */👍
//@@author johndoe /** * Returns true if ... */
What to and what not to annotate
-
Annotate both functional and test code There is no need to annotate documentation files.
-
Annotate only significant size code blocks that can be reviewed on its own e.g., a class, a sequence of methods, a method.
Claiming credit for code blocks smaller than a method is discouraged but allowed. If you do, do it sparingly and only claim meaningful blocks of code such as a block of statements, a loop, or an if-else statement.- If an enhancement required you to do tiny changes in many places, there is no need to annotate all those tiny changes; you can describe those changes in the Project Portfolio page instead.
- If a code block was touched by more than one person, either let the person who wrote most of it (e.g. more than 80%) take credit for the entire block, or leave it as 'unclaimed' (i.e., no author tags).
- Related to the above point, if you claim a code block as your own, more than 80% of the code in that block should have been written by yourself. For example, no more than 20% of it can be code you reused from somewhere.
- 💡 GitHub has a blame feature and a history feature that can help you determine who wrote a piece of code.
-
Do not try to boost the quantity of your contribution using unethical means such as duplicating the same code in multiple places. In particular, do not copy-paste test cases to create redundant tests. Even repetitive code blocks within test methods should be extracted out as utility methods to reduce code duplication. Individual members are responsible for making sure code attributed to them are correct. If you notice a team member claiming credit for code that he/she did not write or use other questionable tactics, you can email us (after the final submission) to let us know.
-
If you wrote a significant amount of code that was not used in the final product,
- Create a folder called
{project root}/unused - Move unused files (or copies of files containing unused code) to that folder
- use
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-unusedto mark unused code in those files (note the suffixunused) e.g.
//@@author johndoe-unused method 1 ... method 2 ...Please put a comment in the code to explain why it was not used.
- Create a folder called
-
If you reused code from elsewhere, mark such code as
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused(note the suffixreused) e.g.//@@author johndoe-reused method 1 ... method 2 ... -
You can use empty
@@authortags to mark code as not yours when RepoSense attribute the to you incorrectly.-
Code generated by the IDE/framework, should not be annotated as your own.
-
Code you modified in minor ways e.g. adding a parameter. These should not be claimed as yours but you can mention these additional contributions in the Project Portfolio page if you want to claim credit for them.
-
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Features implemented: A summary of the features you implemented. If you implemented multiple features, you are recommended to indicate which one is the biggest feature.
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP
-
-
Page limit:
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 (soft limit) Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 (soft limit) Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 (soft limit) Total 5-10 (strict) - The page limits given above are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
- Reason for page limit: These submissions are peer-graded (in the PE) which needs to be done in a limited time span.
If you have more content than the limit given above, you can give a representative samples of UG and DG that showcase your documentation skills. Those samples should be understandable on their own. For the parts left-out, you can give an abbreviated version and refer the reader to the full UG/DG for more details.
It's similar to giving extra details as appendices; the reader will look at the UG/DG if the PPP is not enough to make a judgment. For example, when judging documentation quality, if the part in the PPP is not well-written, there is no point reading the rest in the main UG/DG. That's why you need to put the most representative part of your writings in the PPP and still give an abbreviated version of the rest in the PPP itself. Even when judging the quantity of work, the reader should be able to get a good sense of the quantity by combining what is quoted in the PPP and your abbreviated description of the missing part. There is no guarantee that the evaluator will read the full document.
Follow the
- Get team members to review PRs. A workflow without PR reviews is a risky workflow.
- Do not merge PRs failing
CI . After setting up Travis, the CI status of a PR is reported at the bottom of the PR page. The screenshot below shows the status of a PR that is passing all CI checks.

If there is a failure, you can click on theDetailslink in corresponding line to find out more about the failure. Once you figure out the cause of the failure, push the a fix to the PR. - After setting up Netlify, you can use Netlify PR Preview to preview changes to documentation files, if the PR contains updates to documentation. To see the preview, click on the
Detailslink in front of the Netlify status reported (refer screenshot above).
After completing v1.1, you can adjust process rigor to suit your team's pace, as explained below.
-
Reduce automated tests have benefits, but they can be a pain to write/maintain; GUI tests are especially hard to maintain because their behavior can sometimes depend on things such as the OS, resolution etc.
It is OK to get rid of some of the troublesome tests and rely more on manual testing instead. The less automated tests you have, the higher the risk of regressions; but it may be an acceptable trade-off under the circumstances if tests are slowing you down too much.
There is no direct penalty for removing GUI tests. Also noteour expectation on test code . -
Reduce automated checks: You can also reduce the rigor of checkstyle checks to expedite PR processing.
-
Switch to a lighter workflow: While forking workflow is the safest, it is also rather heavy. You an switch to a simpler workflow if the forking workflow is slowing you down. Refer the textbook to find more about alternative workflows: branching workflow, centralized workflow. However, we still recommend that you use PR reviews, at least for PRs affecting others' features.
You can also increase the rigor/safety of your workflow in the following ways:
- Use GitHub's Protected Branches feature to protect your
masterbranch against rogue PRs.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
Project Management → Revision Control →

In the forking workflow, the 'official' version of the software is kept in a remote repo designated as the 'main repo'. All team members fork the main repo create pull requests from their fork to the main repo.
To illustrate how the workflow goes, let’s assume Jean wants to fix a bug in the code. Here are the steps:
- Jean creates a separate branch in her local repo and fixes the bug in that branch.
- Jean pushes the branch to her fork.
- Jean creates a pull request from that branch in her fork to the main repo.
- Other members review Jean’s pull request.
- If reviewers suggested any changes, Jean updates the PR accordingly.
- When reviewers are satisfied with the PR, one of the members (usually the team lead or a designated 'maintainer' of the main repo) merges the PR, which brings Jean’s code to the main repo.
- Other members, realizing there is new code in the upstream repo, sync their forks with the new upstream repo (i.e. the main repo). This is done by pulling the new code to their own local repo and pushing the updated code to their own fork.
- A detailed explanation of the Forking Workflow - From Atlassian
Documentation:
Recommended procedure for updating docs:
- Divide among yourselves who will update which parts of the document(s).
- Update the team repo by following the workflow mentioned above.
Update the following pages in your project repo:
- About Us page:
This page is used for module admin purposes. Please follow the format closely or else our scripts will not be able to give credit for your work.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
here . - Including the name/photo of the supervisor/lecturer is optional.
- The photo of a team member should be
doc/images/githbub_username_in_lower_case.pnge.g.docs/images/damithc.png. If you photo is in jpg format, name the file as.pnganyway. - Indicate the different roles played and responsibilities held by each team member. You can reassign these
roles and responsibilities (as explained in Admin Project Scope) later in the project, if necessary.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
Roles indicate aspects you are in charge of and responsible for. E.g., if you are in charge of documentation, you are the person who should allocate which parts of the documentation is to be done by who, ensure the document is in right format, ensure consistency etc.
This is a non-exhaustive list; you may define additional roles.
- Team lead: Responsible for overall project coordination.
- Documentation (short for ‘in charge of documentation’): Responsible for the quality of various project documents.
- Testing: Ensures the testing of the project is done properly and on time.
- Code quality: Looks after code quality, ensures adherence to coding standards, etc.
- Deliverables and deadlines: Ensure project deliverables are done on time and in the right format.
- Integration: In charge of versioning of the code, maintaining the code repository, integrating various parts of the software to create a whole.
- Scheduling and tracking: In charge of defining, assigning, and tracking project tasks.
- [Tool ABC] expert: e.g. Intellij expert, Git expert, etc. Helps other team member with matters related to the specific tool.
- In charge of[Component XYZ]: e.g. In charge of
Model,UI,Storage, etc. If you are in charge of a component, you are expected to know that component well, and review changes done to that component in v1.3-v1.4.
Please make sure each of the important roles are assigned to one person in the team. It is OK to have a 'backup' for each role, but for each aspect there should be one person who is unequivocally the person responsible for it.
-
Contact Us Page: Update to match your product.
-
README.adoc page: Update it to match your project.
-
Add a UI mockup of your intended final product.
Note that the image of the UI should bedocs/images/Ui.pngso that it can be downloaded by our scripts. Limit the file to contain one screenshot/mockup only and ensure the new image is roughly the sameheight x widthproportions as the original one. Reason: when we compile these images from all teams into one page (example), yours should not look out of place. -
The original
README.adocfile (which doubles as the landing page of your project website) is written to read like the introduction to an SE learning/teaching resource. You should restructure this page to look like the home page of a real product (not a school project) targeting real users e.g. remove references to addressbook-level3, Learning Outcomes etc. mention target users, add a marketing blurb etc. On a related note, also removeLearning Outcomeslink and related pages. -
Update the link of the Travis build status badge (
) so that it reflects the build status of your team repo.
For the other badges,- either set up the respective tool for your project (AB-4 Developer Guide has instructions on how to set up AppVeyor and Coveralls) and update the badges accordingly,
- or remove the badge.
-
Acknowledge the original source of the code i.e. AddressBook-Level4 project created by SE-EDU initiative at
https://github.com/se-edu/
-
-
User Guide: Start moving the content from your User Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the User Guide page in your repository. If a feature is not implemented, mark it as 'Coming in v2.0' (example).
-
Developer Guide: Similar to the User Guide, start moving the content from your Developer Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the Developer Guide page in your team repository.
Product:
-
Each member can attempt to do a
local-impact change to the code base.Objective: To familiarize yourself with at least one
components of the product.Description: Divide the components among yourselves. Each member can do some small enhancements to their component(s) to learn the code of that component. Some suggested enhancements are given in the AddressBook-Level4 developer guide.
Submission: Create PRs from your own fork to your team repo. Get it merged by following your team's workflow.
5A. Process:
Evaluates: How well you did in project management related aspects of the project, as an individual and as a team
Based on: tutor/bot observations of project milestones and GitHub data
Milestones need to be reached the midnight before of the tutorial for it to be counted as achieved. To get a good grade for this aspect, achieve at least 60% of the recommended milestone progress.
Other criteria:
- Good use of GitHub milestones
- Good use of GitHub release mechanism
- Good version control, based on the repo
- Reasonable attempt to use the forking workflow
- Good task definition, assignment and tracking, based on the issue tracker
- Good use of buffers (opposite: everything at the last minute)
- Project done iteratively and incrementally (opposite: doing most of the work in one big burst)
5B. Team-tasks:
Evaluates: How much you contributed to team-tasks
Based on: peer evaluations, tutor observations
To earn full marks, you should have done a fair share of the team tasks. You can earn bonus marks by doing more than your fair share.
Relevant: [
Here is a non-exhaustive list of team-tasks:
- Necessary general code enhancements e.g.,
- Work related to renaming the product
- Work related to changing the product icon
- Morphing the product into a different product
- Setting up the GitHub, Travis, AppVeyor, etc.
- Maintaining the issue tracker
- Release management
- Updating user/developer docs that are not specific to a feature e.g. documenting the target user profile
- Incorporating more useful tools/libraries/frameworks into the product or the project workflow (e.g. automate more aspects of the project workflow using a GitHub plugin)
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
v1.1 Project Management
- Fix any errors in org/repo set up (e.g. wrong repo name).
- Wrap up the milestone using a git tag
v1.1as explained below:- When the milestone deadline is near (e.g., 0.5 days before the deadline), if you think some of the ongoing work intended for the current milestone may not finish in time, reassign them to a future milestone.
- After all changes that can be merged before the milestone deadline has been merged, use
git tagfeature to tag the current version with the milestone and push the tag to the team repo.
v1.1 Documentation
- Update User Guide, README, and About Us pages as described earlier in
mid-v1.1 progress guide .
Set up project repo, start moving UG and DG to the repo, attempt to do local-impact changes to the code base.
Project Management:
Set up the team org and the team repo as explained below:
Relevant: [
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Relevant: [
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
When updating code in the repo, follow the workflow explained below:
Relevant: [
Workflow
Before you do any coding for the project,
- Ensure you have
set the Git username correctly (as explained in Appendix E) in all Computers you use for coding. - Read
our reuse policy (in Admin: Appendix B) , in particular, how to give credit when you reuse code from the Internet or classmates:
Setting Git Username to Match GitHub Username
We use various tools to analyze your code. For us to be able to identify your commits, you should use the GitHub username as your Git username as well. If there is a mismatch, or if you use multiple user names for Git, our tools might miss some of your work and as a result you might not get credit for some of your work.
In each Computer you use for coding, after installing Git, you should set the Git username as follows.
- Open a command window that can run Git commands (e.g., Git bash window)
- Run the command
git config --global user.name YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME
e.g.,git config --global user.name JohnDoe
More info about setting Git username is here.
Policy on reuse
Reuse is encouraged. However, note that reuse has its own costs (such as the learning curve, additional complexity, usage restrictions, and unknown bugs). Furthermore, you will not be given credit for work done by others. Rather, you will be given credit for using work done by others.
- You are allowed to reuse work from your classmates, subject to following conditions:
- The work has been published by us or the authors.
- You clearly give credit to the original author(s).
- You are allowed to reuse work from external sources, subject to following conditions:
- The work comes from a source of 'good standing' (such as an established open source project). This means you cannot reuse code written by an outside 'friend'.
- You clearly give credit to the original author. Acknowledge use of third party resources clearly e.g. in the welcome message, splash screen (if any) or under the 'about' menu. If you are open about reuse, you are less likely to get into trouble if you unintentionally reused something copyrighted.
- You do not violate the license under which the work has been released. Please do not use 3rd-party images/audio in your software unless they have been specifically released to be used freely. Just because you found it in the Internet does not mean it is free for reuse.
- Always get permission from us before you reuse third-party libraries. Please post your 'request to use 3rd party library' in our forum. That way, the whole class get to see what libraries are being used by others.
Giving credit for reused work
Given below are how to give credit for things you reuse from elsewhere. These requirements are specific to this module i.e., not applicable outside the module (outside the module you should follow the rules specified by your employer and the license of the reused work)
If you used a third party library:
- Mention in the
README.adoc(under the Acknowledgements section) - mention in the
Project Portfolio Page if the library has a significant relevance to the features you implemented
If you reused code snippets found on the Internet e.g. from StackOverflow answers or
referred code in another software or
referred project code by current/past student:
- If you read the code to understand the approach and implemented it yourself, mention it as a comment
Example://Solution below adapted from https://stackoverflow.com/a/16252290 {Your implmentation of the reused solution here ...} - If you copy-pasted a non-trivial code block (possibly with minor modifications renaming, layout changes, changes to comments, etc.), also mark the code block as reused code (using
@@authortags
Format://@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused //{Info about the source...} {Reused code (possibly with minor modifications) here ...} //@@authorpersons = getList() //@@author johndoe-reused //Reused from https://stackoverflow.com/a/34646172 with minor modifications Collections.sort(persons, new Comparator<CustomData>() { @Override public int compare(CustomData lhs, CustomData rhs) { return lhs.customInt > rhs.customInt ? -1 : (lhs.customInt < rhs.customInt) ? 1 : 0; } }); //@@author return persons;
Adding @@author tags indicate authorship
-
Mark your code with a
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}. Note the double@.
The//@@authortag should indicates the beginning of the code you wrote. The code up to the next//@@authortag or the end of the file (whichever comes first) will be considered as was written by that author. Here is a sample code file://@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author sarahkhoo method 3 ... //@@author johndoe method 4 ... -
If you don't know who wrote the code segment below yours, you may put an empty
//@@author(i.e. no GitHub username) to indicate the end of the code segment you wrote. The author of code below yours can add the GitHub username to the empty tag later. Here is a sample code with an emptyauthortag:method 0 ... //@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author method 3 ... method 4 ... -
The author tag syntax varies based on file type e.g. for java, css, fxml. Use the corresponding comment syntax for non-Java files.
Here is an example code from an xml/fxml file.<!-- @@author sereneWong --> <textbox> <label>...</label> <input>...</input> </textbox> ... -
Do not put the
//@@authorinside java header comments.
👎/** * Returns true if ... * @@author johndoe */👍
//@@author johndoe /** * Returns true if ... */
What to and what not to annotate
-
Annotate both functional and test code There is no need to annotate documentation files.
-
Annotate only significant size code blocks that can be reviewed on its own e.g., a class, a sequence of methods, a method.
Claiming credit for code blocks smaller than a method is discouraged but allowed. If you do, do it sparingly and only claim meaningful blocks of code such as a block of statements, a loop, or an if-else statement.- If an enhancement required you to do tiny changes in many places, there is no need to annotate all those tiny changes; you can describe those changes in the Project Portfolio page instead.
- If a code block was touched by more than one person, either let the person who wrote most of it (e.g. more than 80%) take credit for the entire block, or leave it as 'unclaimed' (i.e., no author tags).
- Related to the above point, if you claim a code block as your own, more than 80% of the code in that block should have been written by yourself. For example, no more than 20% of it can be code you reused from somewhere.
- 💡 GitHub has a blame feature and a history feature that can help you determine who wrote a piece of code.
-
Do not try to boost the quantity of your contribution using unethical means such as duplicating the same code in multiple places. In particular, do not copy-paste test cases to create redundant tests. Even repetitive code blocks within test methods should be extracted out as utility methods to reduce code duplication. Individual members are responsible for making sure code attributed to them are correct. If you notice a team member claiming credit for code that he/she did not write or use other questionable tactics, you can email us (after the final submission) to let us know.
-
If you wrote a significant amount of code that was not used in the final product,
- Create a folder called
{project root}/unused - Move unused files (or copies of files containing unused code) to that folder
- use
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-unusedto mark unused code in those files (note the suffixunused) e.g.
//@@author johndoe-unused method 1 ... method 2 ...Please put a comment in the code to explain why it was not used.
- Create a folder called
-
If you reused code from elsewhere, mark such code as
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused(note the suffixreused) e.g.//@@author johndoe-reused method 1 ... method 2 ... -
You can use empty
@@authortags to mark code as not yours when RepoSense attribute the to you incorrectly.-
Code generated by the IDE/framework, should not be annotated as your own.
-
Code you modified in minor ways e.g. adding a parameter. These should not be claimed as yours but you can mention these additional contributions in the Project Portfolio page if you want to claim credit for them.
-
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Features implemented: A summary of the features you implemented. If you implemented multiple features, you are recommended to indicate which one is the biggest feature.
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP
-
-
Page limit:
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 (soft limit) Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 (soft limit) Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 (soft limit) Total 5-10 (strict) - The page limits given above are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
- Reason for page limit: These submissions are peer-graded (in the PE) which needs to be done in a limited time span.
If you have more content than the limit given above, you can give a representative samples of UG and DG that showcase your documentation skills. Those samples should be understandable on their own. For the parts left-out, you can give an abbreviated version and refer the reader to the full UG/DG for more details.
It's similar to giving extra details as appendices; the reader will look at the UG/DG if the PPP is not enough to make a judgment. For example, when judging documentation quality, if the part in the PPP is not well-written, there is no point reading the rest in the main UG/DG. That's why you need to put the most representative part of your writings in the PPP and still give an abbreviated version of the rest in the PPP itself. Even when judging the quantity of work, the reader should be able to get a good sense of the quantity by combining what is quoted in the PPP and your abbreviated description of the missing part. There is no guarantee that the evaluator will read the full document.
Follow the
- Get team members to review PRs. A workflow without PR reviews is a risky workflow.
- Do not merge PRs failing
CI . After setting up Travis, the CI status of a PR is reported at the bottom of the PR page. The screenshot below shows the status of a PR that is passing all CI checks.

If there is a failure, you can click on theDetailslink in corresponding line to find out more about the failure. Once you figure out the cause of the failure, push the a fix to the PR. - After setting up Netlify, you can use Netlify PR Preview to preview changes to documentation files, if the PR contains updates to documentation. To see the preview, click on the
Detailslink in front of the Netlify status reported (refer screenshot above).
After completing v1.1, you can adjust process rigor to suit your team's pace, as explained below.
-
Reduce automated tests have benefits, but they can be a pain to write/maintain; GUI tests are especially hard to maintain because their behavior can sometimes depend on things such as the OS, resolution etc.
It is OK to get rid of some of the troublesome tests and rely more on manual testing instead. The less automated tests you have, the higher the risk of regressions; but it may be an acceptable trade-off under the circumstances if tests are slowing you down too much.
There is no direct penalty for removing GUI tests. Also noteour expectation on test code . -
Reduce automated checks: You can also reduce the rigor of checkstyle checks to expedite PR processing.
-
Switch to a lighter workflow: While forking workflow is the safest, it is also rather heavy. You an switch to a simpler workflow if the forking workflow is slowing you down. Refer the textbook to find more about alternative workflows: branching workflow, centralized workflow. However, we still recommend that you use PR reviews, at least for PRs affecting others' features.
You can also increase the rigor/safety of your workflow in the following ways:
- Use GitHub's Protected Branches feature to protect your
masterbranch against rogue PRs.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
Project Management → Revision Control →

In the forking workflow, the 'official' version of the software is kept in a remote repo designated as the 'main repo'. All team members fork the main repo create pull requests from their fork to the main repo.
To illustrate how the workflow goes, let’s assume Jean wants to fix a bug in the code. Here are the steps:
- Jean creates a separate branch in her local repo and fixes the bug in that branch.
- Jean pushes the branch to her fork.
- Jean creates a pull request from that branch in her fork to the main repo.
- Other members review Jean’s pull request.
- If reviewers suggested any changes, Jean updates the PR accordingly.
- When reviewers are satisfied with the PR, one of the members (usually the team lead or a designated 'maintainer' of the main repo) merges the PR, which brings Jean’s code to the main repo.
- Other members, realizing there is new code in the upstream repo, sync their forks with the new upstream repo (i.e. the main repo). This is done by pulling the new code to their own local repo and pushing the updated code to their own fork.
- A detailed explanation of the Forking Workflow - From Atlassian
Documentation:
Recommended procedure for updating docs:
- Divide among yourselves who will update which parts of the document(s).
- Update the team repo by following the workflow mentioned above.
Update the following pages in your project repo:
- About Us page:
This page is used for module admin purposes. Please follow the format closely or else our scripts will not be able to give credit for your work.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
here . - Including the name/photo of the supervisor/lecturer is optional.
- The photo of a team member should be
doc/images/githbub_username_in_lower_case.pnge.g.docs/images/damithc.png. If you photo is in jpg format, name the file as.pnganyway. - Indicate the different roles played and responsibilities held by each team member. You can reassign these
roles and responsibilities (as explained in Admin Project Scope) later in the project, if necessary.
- Replace info of SE-EDU developers with info of your team, including a suitable photo as described
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
Roles indicate aspects you are in charge of and responsible for. E.g., if you are in charge of documentation, you are the person who should allocate which parts of the documentation is to be done by who, ensure the document is in right format, ensure consistency etc.
This is a non-exhaustive list; you may define additional roles.
- Team lead: Responsible for overall project coordination.
- Documentation (short for ‘in charge of documentation’): Responsible for the quality of various project documents.
- Testing: Ensures the testing of the project is done properly and on time.
- Code quality: Looks after code quality, ensures adherence to coding standards, etc.
- Deliverables and deadlines: Ensure project deliverables are done on time and in the right format.
- Integration: In charge of versioning of the code, maintaining the code repository, integrating various parts of the software to create a whole.
- Scheduling and tracking: In charge of defining, assigning, and tracking project tasks.
- [Tool ABC] expert: e.g. Intellij expert, Git expert, etc. Helps other team member with matters related to the specific tool.
- In charge of[Component XYZ]: e.g. In charge of
Model,UI,Storage, etc. If you are in charge of a component, you are expected to know that component well, and review changes done to that component in v1.3-v1.4.
Please make sure each of the important roles are assigned to one person in the team. It is OK to have a 'backup' for each role, but for each aspect there should be one person who is unequivocally the person responsible for it.
-
Contact Us Page: Update to match your product.
-
README.adoc page: Update it to match your project.
-
Add a UI mockup of your intended final product.
Note that the image of the UI should bedocs/images/Ui.pngso that it can be downloaded by our scripts. Limit the file to contain one screenshot/mockup only and ensure the new image is roughly the sameheight x widthproportions as the original one. Reason: when we compile these images from all teams into one page (example), yours should not look out of place. -
The original
README.adocfile (which doubles as the landing page of your project website) is written to read like the introduction to an SE learning/teaching resource. You should restructure this page to look like the home page of a real product (not a school project) targeting real users e.g. remove references to addressbook-level3, Learning Outcomes etc. mention target users, add a marketing blurb etc. On a related note, also removeLearning Outcomeslink and related pages. -
Update the link of the Travis build status badge (
) so that it reflects the build status of your team repo.
For the other badges,- either set up the respective tool for your project (AB-4 Developer Guide has instructions on how to set up AppVeyor and Coveralls) and update the badges accordingly,
- or remove the badge.
-
Acknowledge the original source of the code i.e. AddressBook-Level4 project created by SE-EDU initiative at
https://github.com/se-edu/
-
-
User Guide: Start moving the content from your User Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the User Guide page in your repository. If a feature is not implemented, mark it as 'Coming in v2.0' (example).
-
Developer Guide: Similar to the User Guide, start moving the content from your Developer Guide (draft created in previous weeks) into the Developer Guide page in your team repository.
Product:
-
Each member can attempt to do a
local-impact change to the code base.Objective: To familiarize yourself with at least one
components of the product.Description: Divide the components among yourselves. Each member can do some small enhancements to their component(s) to learn the code of that component. Some suggested enhancements are given in the AddressBook-Level4 developer guide.
Submission: Create PRs from your own fork to your team repo. Get it merged by following your team's workflow.
-
Update Developer Guide page with user stories and use cases. Refer to
mid-v1.0. Submission: Merge your changes to the master branch of your repo. Create a PR with your changes.
Decide on requirements (user stories, use cases, non-functional requirements).
💡 Given below are some guidance on the recommended progress at this point of the project (i.e., at week 4, which is the midway point of the milestone v1.0)
This is a good time to analyze requirements with a view to conceptualizing the next version of the product (i.e. v2.0).
-
Step 1 : Brainstorm user stories

Get together with your team members and
brainstorm foruser stories for the v2.0 of the product. Note that in the module project you will deliver only up to v1.4 but here you should consider up to v2.0 (i.e. beyond the module).-
It is ok to have more user stories than you can deliver in the project. Aim to create at least 30 user stories. Include all 'obvious' ones you can think of but also look for 'non obvious' ones that you think are likely to be missed by other teams.
-
Refer
[Textbook Specifying Requirements → UserStories → Usage → (section) Tips] for tips on how to use user stories in this task. -
You can write each user story in a piece of paper (e.g. yellow sticky note, index card, or just pieces of paper about the size of a playing card). Alternatively you can use an online tool (some examples given in
[Textbook Specifying Requirements → UserStories → Usage → (panel) Tool Examples ] ). -
Note that you should not 'evaluate' the value of user stories while doing the above. Reason: an important aspect of brainstorming is not judging the ideas generated.
-
Requirements → Gathering Requirements →
Brainstorming: A group activity designed to generate a large number of diverse and creative ideas for the solution of a problem.
In a brainstorming session there are no "bad" ideas. The aim is to generate ideas; not to validate them. Brainstorming encourages you to "think outside the box" and put "crazy" ideas on the table without fear of rejection.
What is the key characteristic about brainstorming?
(b)
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → User Stories →
User story: User stories are short, simple descriptions of a feature told from the perspective of the person who desires the new capability, usually a user or customer of the system. [Mike Cohn]
A common format for writing user stories is:
User story format: As a {user type/role} I can {function} so that {benefit}
Examples (from a Learning Management System):
- As a student, I can download files uploaded by lecturers, so that I can get my own copy of the files
- As a lecturer, I can create discussion forums, so that students can discuss things online
- As a tutor, I can print attendance sheets, so that I can take attendance during the class
We can write user stories on index cards or sticky notes, and arrange on walls or tables, to facilitate planning and discussion. Alternatively, we can use a software (e.g., GitHub Project Boards, Trello, Google Docs, ...) to manage user stories digitally.


[credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jakuza/with/2726048607/]

[credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:User_Story_Map_in_Action.png]
- a. They are based on stories users tell about similar systems
- b. They are written from the user/customer perspective
- c. They are always written in some physical medium such as index cards or sticky notes
- a. Reason: Despite the name, user stories are not related to 'stories' about the software.
- b.
- c. Reason: It is possible to use software to record user stories. When the team members are not co-located this may be the only option.
Critique the following user story taken from a software project to build an e-commerce website.
As a developer, I want to use Python to implement the software, so that we can resue existing Python modules.
Refer to the definition of a user story.
User story: User stories are short, simple descriptions of a feature told from the perspective of the person who desires the new capability, usually a user or customer of the system. [Mike Cohn]
This user story is not written from the perspective of the user/customer.
Bill wants you to build a Human Resource Management (HRM) system. He mentions that the system will help employees to view their own
Remember to follow the correct format when writing user stories.
User story format: As a {user type/role} I can {function} so that {benefit}
As an employee, I can view my leave balance, so that I can know how many leave days I have left.
Note: the {benefit} part may vary as it is not specifically mentioned in the question.
You can create issues for each of the user stories and use a GitHub Project Board to sort them into categories.
Example Project Board:

Example Issue to represent a user story:

A video on GitHub Project Boards:
Example Google Sheet for recording user stories:

Example Trello Board for recording user stories:

Given their lightweight nature, user stories are quite handy for recording requirements during early stages of requirements gathering.
💡 Here are some tips for using user stories for early stages of requirement gathering:
- Define the target user:
Decide your target user's profile (e.g. a student, office worker, programmer, sales person) and work patterns (e.g. Does he work in groups or alone? Does he share his computer with others?). A clear understanding of the target user will help when deciding the importance of a user story. You can even give this user a name. e.g. Target user Jean is a university student studying in a non-IT field. She interacts with a lot of people due to her involvement in university clubs/societies. ... - Define the problem scope: Decide that exact problem you are going to solve for the target user. e.g. Help Jean keep track of all her school contacts
- Don't be too hasty to discard 'unusual' user stories:
Those might make your product unique and stand out from the rest, at least for the target users. - Don't go into too much details:
For example, consider this user story:As a user, I want to see a list of tasks that needs my attention most at the present time, so that I pay attention to them first.
When discussing this user story, don't worry about what tasks should be considered needs my attention most at the present time. Those details can be worked out later. - Don't be biased by preconceived product ideas:
When you are at the stage of identifying user needs, clear your mind of ideas you have about what your end product will look like. - Don't discuss implementation details or whether you are actually going to implement it:
When gathering requirements, your decision is whether the user's need is important enough for you to want to fulfil it. Implementation details can be discussed later. If a user story turns out to be too difficult to implement later, you can always omit it from the implementation plan.
💡 Recommended: You can use GitHub issue tracker to manage user stories, but for that you need to set up your team's GitHub organization, project fork, and issue tracker first. Instructions for doing those steps are in the panel below.
Organization setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely because we use scripts to download your code or else our scripts will not be able to detect your work.
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name :
CS2103-AY1819S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.CS2103-AY1819S2-W12-1 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- Organization name :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
Repo setup
Only one team member:
- Fork Address Book Level 4 to your team org.
- Rename the forked repo as
main. This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project. - Ensure the issue tracker of your team repo is enabled. Reason: our bots will be posting your weekly progress reports on the issue tracker of your team repo.
- Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
- Enable Travis CI for the team repo.
- Set up auto-publishing of docs. When set up correctly, your project website should be available via the URL
https://cs2103-ay1819s2-{team-id}.github.io/maine.g.,https://cs2103-ay1819s2-w13-1.github.io/main/. This also requires you to enable the GitHub Pages feature of your team repo and configure it to serve the website from thegh-pagesbranch. - Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2103-AY1819S2/addressbook-level4]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[T09-2] Contact List Pro. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed. In the PR description@mention the other team members so that they get notified when the tutor adds comments to the PR.
All team members:
- Watch the
mainrepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on thewatchbutton to subscribe to activities of the repo - Fork the
mainrepo to your personal GitHub account. - Clone the fork to your Computer.
- Recommended: Set it up as an Intellij project (follow the instructions in the Developer Guide carefully).
- Set up the developer environment in your computer. You are recommended to use JDK 9 for AB-4 as some of the libraries used in AB-4 have not updated to support Java 10 yet. JDK 9 can be downloaded from the Java Archive.
Note that some of our download scripts depend on the following folder paths. Please do not alter those paths in your project.
/src/main/src/test/docs
Issue tracker setup
We recommend you configure the issue tracker of the main repo as follows:
- Delete existing labels and add the following labels.
💡 Issue type labels are useful from the beginning of the project. The other labels are needed only when you start implementing the features.
Issue type labels:
type.Epic: A big feature which can be broken down into smaller stories e.g. searchtype.Story: A user storytype.Enhancement: An enhancement to an existing storytype.Task: Something that needs to be done, but not a story, bug, or an epic. e.g. Move testing code into a new folder)type.Bug: A bug
Status labels:
status.Ongoing: The issue is currently being worked on. note: remove this label before closing an issue.
Priority labels:
priority.High: Must dopriority.Medium: Nice to havepriority.Low: Unlikely to do
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Create following milestones :
v1.0,v1.1,v1.2,v1.3,v1.4, -
You may configure other project settings as you wish. e.g. more labels, more milestones
Project Schedule Tracking
In general, use the issue tracker (Milestones, Issues, PRs, Tags, Releases, and Labels) for assigning, scheduling, and tracking all noteworthy project tasks, including user stories. Update the issue tracker regularly to reflect the current status of the project. You can also use GitHub's Projects feature to manage the project, but keep it linked to the issue tracker as much as you can.
Using Issues:
During the initial stages (latest by the start of v1.2):
-
Record each of the user stories you plan to deliver as an issue in the issue tracker. e.g.
Title: As a user I can add a deadline
Description: ... so that I can keep track of my deadlines -
Assign the
type.*andpriority.*labels to those issues. -
Formalize the project plan by assigning relevant issues to the corresponding milestone.
From milestone v1.2:
-
Define project tasks as issues. When you start implementing a user story (or a feature), break it down to smaller tasks if necessary. Define reasonable sized, standalone tasks. Create issues for each of those tasks so that they can be tracked.e.g.
-
A typical task should be able to done by one person, in a few hours.
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
Write the Developer Guide - Good:
Update class diagram in the Developer Guide for v1.4
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
-
There is no need to break things into VERY small tasks. Keep them as big as possible, but they should be no bigger than what you are going to assign a single person to do within a week. eg.,
- Bad:
Implementing parser(reason: too big). - Good:
Implementing parser support for adding of floating tasks
- Bad:
-
Do not track things taken for granted. e.g.,
push code to reposhould not be a task to track. In the example given under the previous point, it is taken for granted that the owner will also (a) test the code and (b) push to the repo when it is ready. Those two need not be tracked as separate tasks. -
Write a descriptive title for the issue. e.g.
Add support for the 'undo' command to the parser- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
prioritycan be omitted if you think they don't help you.
- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
-
-
Assign tasks (i.e., issues) to the corresponding team members using the
assigneesfield. Normally, there should be some ongoing tasks and some pending tasks against each team member at any point. -
Optionally, you can use
status.ongoinglabel to indicate issues currently ongoing.
Using Milestones:
We recommend you do proper milestone management starting from v1.2. Given below are the conditions to satisfy for a milestone to be considered properly managed:
Planning a Milestone:
-
Issues assigned to the milestone, team members assigned to issues: Used GitHub milestones to indicate which issues are to be handled for which milestone by assigning issues to suitable milestones. Also make sure those issues are assigned to team members. Note that you can change the milestone plan along the way as necessary.
-
Deadline set for the milestones (in the GitHub milestone). Your internal milestones can be set earlier than the deadlines we have set, to give you a buffer.
Wrapping up a Milestone:
-
A working product tagged with the correct tag (e.g.
v1.2) and is pushed to the main repo
or a product release done on GitHub. A product release is optional for v1.2 but required from from v1.3. Click here to see an example release. -
All tests passing on Travis for the version tagged/released.
-
Milestone updated to match the product i.e. all issues completed and PRs merged for the milestone should be assigned to the milestone. Incomplete issues/PRs should be moved to a future milestone.

-
Milestone closed.

-
If necessary, future milestones are revised based on what you experienced in the current milestone e.g. if you could not finish all issues assigned to the current milestone, it is a sign that you overestimated how much you can do in a week, which means you might want to reduce the issues assigned to future milestones to match that observation.
As a user I can add a task by specifying a task description only, so that I can record tasks that need to be done ‘some day’.
As a user I can find upcoming tasks, so that I can decide what needs to be done soon.
As a user I can delete a task, so that I can get rid of tasks that I no longer care to track.
As a new user I can view more information about a particular command, so that I can learn how to use various commands.
As an advanced user I can use shorter versions of a command, so that type a command faster.
-
Step 2: Prioritize the user stories

Suggested workflow:
-
Take one user story at a time and get team member opinions about it.
-
Based on the team consensus, put the story (i.e. the piece of paper) onto one of these three piles:
Must-Have: The product will be practically useless to the target user without this feature.Nice-To-Have: The target user can benefit from this user story significantly but you are not certain if you'll have time to implement it.Not-Useful: No significant benefit to the target user, or does not fit into the product vision.
-
If using physical paper to record user stories: After all stories have been put in the above three piles, you can make a record of which stories are in the three piles.
-
-
Step 3: Document requirements of the product
Based on your user story categorization in the step above, given module requirements/constraints for the project, and the current state of the product, select which user stories you are likely to include in v2.0.
Document the following items using a convenient format (e.g., a GoogleDoc). Do not spend time on formatting the content nicely; reason: these will be ported to the actual Developer Guide in your project repo later.
💡 Some examples of these can be found in the AB4 Developer Guide.- Target user profile, value proposition, and
user stories : Update the target user profile and value proposition to match the project direction you have selected. Give a list of the user stories (and update/delete existing ones, if applicable), including priorities. This can include user stories considered but will not be included in the final product. -
Use cases : Give use cases (textual form) for a few representative user stories that need multiple steps to complete. e.g. Adding a tag to a person (assume the user needs to find the person first) -
Non-functional requirements :
Note: Many of the project constraints mentioned above are NFRs. You can add more. e.g. performance requirements, usability requirements, scalability requirements, etc. -
Glossary : Define terms that are worth defining. - [Optional]
Product survey : Explore a few similar/related products and describe your findings i.e. Pros, cons, (from the target user's point of view).
- Target user profile, value proposition, and
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → Use Cases →
Use Case: A description of a set of sequences of actions, including variants, that a system performs to yield an observable result of value to an
Actor: An actor (in a use case) is a role played by a user. An actor can be a human or another system. Actors are not part of the system; they reside outside the system.
A use case describes an interaction between the user and the system for a specific functionality of the system.
- System:
ATM - Actor: Customer
- Use Case: Check account balance
- User inserts an ATM card
- ATM prompts for PIN
- User enters PIN
- ATM prompts for withdrawal amount
- User enters the amount
- ATM ejects the ATM card and issues cash
- User collects the card and the cash.
- System: A Learning Management System (LMS)
- Actor: Student
- Use Case: Upload file
- Student requests to upload file
- LMS requests for the file location
- Student specifies the file location
- LMS uploads the file
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a graphical notation to describe various aspects of a software system. UML is the brainchild of three software modeling specialists James Rumbaugh, Grady Booch and Ivar Jacobson (also known as the Three Amigos). Each of them has developed their own notation for modeling software systems before joining force to create a unified modeling language (hence, the term ‘Unified’ in UML). UML is currently the de facto modeling notation used in the software industry.

Use cases capture the functional requirements of a system.
Requirements → Requirements →
There are two kinds of requirements:
- Functional requirements specify what the system should do.
- Non-functional requirements specify the constraints under which system is developed and operated.
Some examples of non-functional requirement categories:
- Data requirements e.g. size,
volatility ,persistency etc., - Environment requirements e.g. technical environment in which system would operate or need to be compatible with.
- Accessibility, Capacity, Compliance with regulations, Documentation, Disaster recovery, Efficiency, Extensibility, Fault tolerance, Interoperability, Maintainability, Privacy, Portability, Quality, Reliability, Response time, Robustness, Scalability, Security, Stability, Testability, and more ...
- Business/domain rules: e.g. the size of the minefield cannot be smaller than five.
- Constraints: e.g. the system should be backward compatible with data produced by earlier versions of the system; system testers are available only during the last month of the project; the total project cost should not exceed $1.5 million.
- Technical requirements: e.g. the system should work on both 32-bit and 64-bit environments.
- Performance requirements: e.g. the system should respond within two seconds.
- Quality requirements: e.g. the system should be usable by a novice who has never carried out an online purchase.
- Process requirements: e.g. the project is expected to adhere to a schedule that delivers a feature set every one month.
- Notes about project scope: e.g. the product is not required to handle the printing of reports.
- Any other noteworthy points: e.g. the game should not use images deemed offensive to those injured in real mine clearing activities.
We may have to spend an extra effort in digging NFRs out as early as possible because,
- NFRs are easier to miss e.g., stakeholders tend to think of functional requirements first
- sometimes NFRs are critical to the success of the software. E.g. A web application that is too slow or that has low security is unlikely to succeed even if it has all the right functionality.
Given below are some requirements of TEAMMATES (an online peer evaluation system for education). Which one of these are non-functional requirements?
- a. The response to any use action should become visible within 5 seconds.
- b. The application admin should be able to view a log of user activities.
- c. The source code should be open source.
- d. A course should be able to have up to 2000 students.
- e. As a student user, I can view details of my team members so that I can know who they are.
- f. The user interface should be intuitive enough for users who are not IT-savvy.
- g. The product is offered as a free online service.
(a)(c)(d)(f)(g)
Explanation: (b) are (e) are functions available for a specific user types. Therefore, they are functional requirements. (a), (c), (d), (f) and (g) are either constraints on functionality or constraints on how the project is done, both of which are considered non-functional requirements.
Requirements → Specifying Requirements → Glossary →
Glossary: A glossary serves to ensure that all stakeholders have a common understanding of the noteworthy terms, abbreviation, acronyms etc.
Here is a partial glossary from a variant of the Snakes and Ladders game:
- Conditional square: A square that specifies a specific face value which a player has to throw before his/her piece can leave the square.
- Normal square: a normal square does not have any conditions, snakes, or ladders in it.
Requirements → Gathering Requirements →
Studying existing products can unearth shortcomings of existing solutions that can be addressed by a new product. Product manuals and other forms of technical documentation of an existing system can be a good way to learn about how the existing solutions work.
When developing a game for a mobile device, a look at a similar PC game can give insight into the kind of features and interactions the mobile game can offer.
Tutors will provide feedback on this version of the UG and DG. This feedback should be used to improve your final submission.
v1.1 Product
- Each member should try to add some enhancements that are in line with the vision for v2.0. After adding some local-impact changes as recommended in
mid-v1.1 progress guide , attempt to do someglobal-impact enhancements , touching as many other components as possible. Refer to the AddressBook-Level4 Developer Guide has some guidance on how to implement a new feature end-to-end.
If your team is facing difficulties due to differences in skill/motivation /availability among team members,
-
First, do not expect everyone to have the same skill/motivation level as you. It is fine if someone wants to do less and have low expectations from the module. That doesn't mean that person is a bad person. Everyone is entitled to have their own priorities.
-
Second, don't give up. It is unfortunate that your team ended up in this situation, but you can turn it into a good learning opportunity. You don't get an opportunity to save a sinking team every day 😃
-
Third, if you care about your grade and willing to work for it, you need to take initiative to turn the situation around or else the whole team is going to suffer. Don't hesitate to take charge if the situation calls for it. By doing so, you'll be doing a favor for your team. Be professional, kind, and courteous to the team members, but also be firm and assertive. It is your grade that is at stake. Don't worry about making a bad situation worse. You won't know until you try.
-
Finally, don't feel angry or 'wronged'. Teamwork problems are not uncommon in this module and we know how to grade so that you will not be penalized for others' low contribution. We can use Git to find exactly what others did. It's not your responsibility to get others to contribute.
Given below are some suggestions you can adopt if the project work is not going smooth due to team issues. Note that the below measures can result in some team members doing more work than others and earning better project grades than others. It is still better than sinking the whole team together.
-
Redistribute the work: Stronger programmers in the team should take over the critical parts of the code.
-
Enforce stricter integration workflow: Appoint an integrator (typically, the strongest programmer). His/her job is to maintain the integrated version of the code. He/she should not accept any code that breaks the existing product or is not up to the acceptable quality standard. It is up to others to submit acceptable code to the integrator. Note that if the integrator rejected your code unreasonably, you can still earn marks for that code. You are allowed to submit such 'rejected' code for grading. They can earn marks based on the quality of the code.
If you have very unreliable or totally disengaged team members :
- Re-allocate to others any mission-critical work allocated to that person so that such team members cannot bring down the entire team.
- However, do not leave out such team members from project communications. Always keep them in the loop so that they can contribute any time they wish to.
- Furthermore, evaluate them sincerely and fairly during peer evaluations so that they do get the grade their work deserves, no more, no less.
- Be courteous to such team members too. Some folks have genuine problems that prevent them from contributing more although they may not be able tell you the reasons. Just do your best for the project and assume everyone else is doing their best too, although their best may be lower than yours.
Why I’m not allowed to use my favorite tool/framework/language etc.?
We have chosen a basic set of tools after considering ease of learning, availability, typical-ness, popularity, migration path to other tools, etc. There are many reasons for limiting your choices:
Pedagogical reasons:
- Sometimes 'good enough', not necessarily the best, tools are a better fit for beginners: Most bleeding edge, most specialized, or most sophisticated tools are not suitable for a beginner course. After mastering our toolset, you will find it easy to upgrade to such high-end tools by yourself. We do expect you to eventually (after this module) migrate to better tools and, having learned more than one tool, to attain a more general understanding about a family of tools.
- We want you to learn to thrive under given conditions: As a professional Software Engineer, you must learn to be productive in any given tool environment, rather than insist on using your preferred tools. It is usually in small companies doing less important work that you get to chose your own toolset. Bigger companies working on mature products often impose some choices on developers, such as the project management tool, code repository, IDE, language etc. For example, Google used SVN as their revision control software until very recently, long after SVN fell out of popularity among developers. Sometimes this is due to cost reasons (tool licensing cost), and sometimes due to legacy reasons (because the tool is already entrenched in their code base).
While programming in school is often a solo sport, programming in the industry is a team sport. As we are training you to become professional software engineers, it is important to get over the psychological hurdle of needing to satisfy individual preferences and get used to making the best of a given environment.
Practical reasons:
- Some of the topics are tightly coupled to tools. Allowing more tools means tutors need to learn more tools, which increases their workload.
- We provide learning resources for tools. e.g. 'Git guides'. Allowing more tools means we need to produce more resources.
- When all students use the same tool, the collective expertise of the tool is more, increasing the opportunities for you to learn from each others.
Meanwhile, feel free to share with peers your experience of using other tools.